Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Correction: Functional synthetic probes for selective targeting and multi-analyte detection and imaging
Yongkang
Yue
a,
Fangjun
Huo
b,
Fangqin
Cheng
c,
Xijing
Zhu
d,
Tendai
Mafireyi
d,
Robert M.
Strongin
*d and
Caixia
Yin
*a
aKey Laboratory of Chemical Biology and Molecular Engineering of Ministry of Education, Key Laboratory of Materials for Energy Conversion and Storage of Shanxi Province, Institute of Molecular Science of Shanxi University, Taiyuan, Shanxi 030006, China. E-mail: yincx@sxu.edu.cn
bResearch Institute of Applied Chemistry, Shanxi University, Taiyuan, 030006, China
cInstitute of Resources and Environment Engineering, Shanxi University, Taiyuan, 030006, China
dDepartment of Chemistry, Portland State University, Portland, Oregon 97201, USA. E-mail: strongin@pdx.edu
First published on 5th July 2019
Abstract
Correction for ‘Functional synthetic probes for selective targeting and multi-analyte detection and imaging’ by Yongkang Yue et al., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, DOI: 10.1039/c8cs01006d.
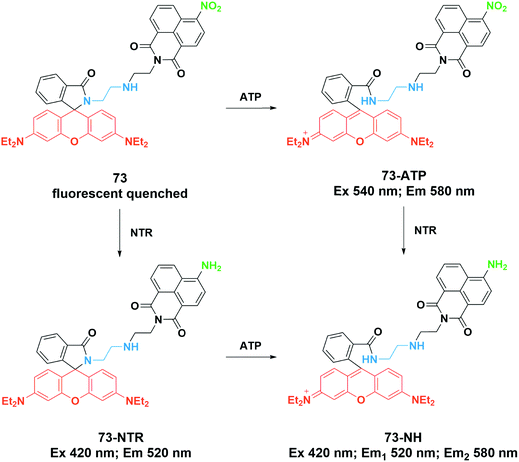
The authors regret that Fig. 44 in the original article was incorrect. A FRET mechanism was not proposed by the authors of the cited article.1 A second emission wavelength was additionally determined. The correct version of Fig. 44 is presented below.
The Royal Society of Chemistry apologises for these errors and any consequent inconvenience to authors and readers.
References
- Y. Fang, W. Shi, Y. Hu, X. Li and H. Ma, Chem. Commun., 2018, 54, 5454–5457 RSC.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 |