Structural phase transitions in VSe2: energetics, electronic structure and magnetism†
Abstract
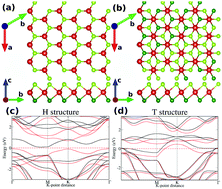
First principles calculations of the magnetic and electronic properties of VSe2 describing the transition between two structural phases (H,T) were performed. The results of the calculations evidence a rather low energy barrier (0.60 eV for the monolayer) for the transition between the phases. The energy required for the deviation of a Se atom or whole layer of selenium atoms by a small angle of up to 10° from their initial positions is also rather low, 0.32 and 0.19 eV/Se, respectively. The changes in the band structure of VSe2 caused by these motions of Se atoms should be taken into account for analysis of the experimental data. Simulations of the strain effects suggest that the experimentally observed T phase of the VSe2 monolayer is the ground state due to substrate-induced strain. Calculations of the difference in the total energies of the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic configurations evidence that the ferromagnetic configuration is the ground state of the system for all stable and intermediate atomic structures. Calculated phonon dispersions suggest a visible influence of the magnetic configurations on the vibrational properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...