ZSM-5 decrystallization and dealumination in hot liquid water†
Abstract
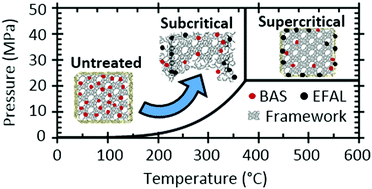
Zeolites have recently attracted attention for upgrading renewable resources in the presence of liquid water phases; however, the stability of zeolites in the presence of liquid-phase water is not completely understood. Accordingly, the stability of the ZSM-5 framework and its acid sites was studied in the presence of water at temperatures ranging from 250 to 450 °C and at pressures sufficient to maintain a liquid or liquid-like state (25 MPa). Treated samples were analyzed for framework degradation and Al content and coordination using a variety of complementary techniques, including X-ray diffraction, electron microscopy, N2 sorption, 27Al and 29Si NMR spectroscopy, and several different types of infrared spectroscopy. These analyses indicate that the ZSM-5 framework retains >80% crystallinity at all conditions, and that 300–400 °C are the most aggressive. Decrystallization appears to initiate primarily at crystal surfaces and share many characteristics in common with alkali promoted desilication. Liquid water treatment promotes ZSM-5 dealumination, following a mechanism analogous to that observed under steaming conditions: initiation by Al–O hydrolysis, Al migration to the surface, and finally deposition as extra framework Al or possibly complete dissolution under some conditions. As with the framework, dealumination is most aggressive at 300–400 °C. Several models were evaluated to capture the non-Arrhenius effect of temperature on decrystallization and dealumination, the most successful of which included temperature dependent values of the water auto-ionization constant. These results can help interpretation of previous studies on ZSM-5 catalysis in hot liquid water and suggest future approaches to extend catalyst lifetime.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...