Photo induced chemical modification of surface ligands for aggregation and luminescence modulation of copper nanoclusters in the presence of oxygen†
Abstract
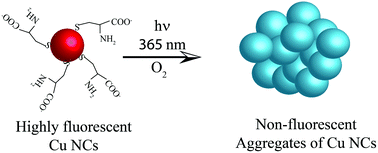
Surface modification of nanoparticles has been a popular approach to tailor the properties of nanoparticles. Herein we report the unprecedented photo oxidation of cysteine moeties on the surface of copper nanoclusters (Cu NCs) leading to aggregation of Cu NCs, which further led to quenching of luminescence of the latter. Upon illumination of a dispersion of Cu NCs at 365 nm wavelength light, the luminescence of Cu NCs was completely quenched. Furthermore, the extent of luminescence quenching of Cu NCs upon photo illumination could be tuned by varying the area of exposure of light. Confirmation of photooxidation of cysteine molecules was made through Fourier transformed infrared (FTIR) studies, while the formation of submicron sized aggregates of Cu NCs as a result of photo oxidation of cysteine stabilizing the nanoclusters was evinced through transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The study embodied herein opens up new avenues for the tailoring of the chemical and optical properties of metal nanoclusters through chemical transformation of surface ligand moieties, which is envisioned to emerge as a powerful strategy for broadening the application potential of metal nanoclusters.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...