High-throughput computational screening of metal–organic frameworks with topological diversity for hexane isomer separations†
Abstract
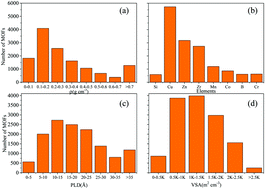
The adsorption separation of C6–C8 hydrocarbons in metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) has attracted extensive attention worldwide due to its technical feasibility and high energy efficiency in the petroleum industry. In this study, a large-scale computational screening of 13 512 MOFs with topological diversity was carried out to search optimal candidates for the simultaneous separation of two dimethyl butanes (DMB) from the quinary equimolar mixture of hexane isomers. We first screened out 841 MOFs according to their geometrical properties such as pore limited diameter (PLD) and volumetric surface area. Subsequently, high-performing MOFs were ranked out by an evaluation metric of adsorption performance score (APS), that is the product of the adsorption capacity of DMB and the selectivity of DMB over normal and mono-branched hexane isomers (N + M), on the basis of the predicted capacities by the grand canonical Monte Carlo (GCMC) simulations at 10 bar and 433 K. The structure–property relationships were established between APS and MOF descriptors such as density, PLD, etc. Among the screened 841 MOFs, the MOF with highest APS was MOF-163 because it provided an ideal pore topology with the 6.85 Å annular channel to distinguish DMB from the N + M isomers. The breakthrough predictions further demonstrated that the dimensionless residence time of 2,2-dimethylbutane (22DMB) was significantly different from that of n-hexane; this indicated that MOF-163 was a superior candidate for the dynamic separation of hexane isomers. Radial distribution function, adsorption equilibrium configurations and mass center probability density distributions were investigated to elucidate why MOF-163 could differentiate DBM from the N + M isomers. The molecular-level insights proposed in this study will facilitate the development of new MOFs for the separation of hydrocarbons in the petroleum industry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...