Two photon excitable graphene quantum dots for structured illumination microscopy and imaging applications: lysosome specificity and tissue-dependent imaging†
Abstract
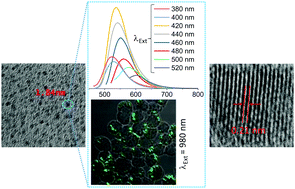
Biocompatible graphene quantum dots (GQDs), obtained from extracts of neem root, are found to be suitable for structured illumination microscopy and two-photon microscopy (TPM). Results of TPM and confocal luminescence microscopy ensure lysosome specificity in live cells and tissue-dependent localization in zebrafish, respectively, of GQDs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...