Two fluorescence quenching immunochromatographic assays based on carbon dots and quantum dots as donor probes for the determination of enrofloxacin†
Abstract
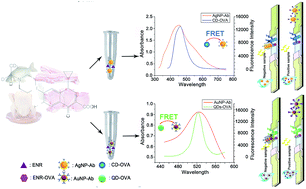
Two “turn-on” pattern fluorescence-quenching lateral flow immunochromatographic assays (FLFIAs) based on carbon dot (CD)/silver nanoparticle (AgNP) and quantum dot (QD)/gold nanoparticle (AuNP) fluorescence quenching systems were developed for the specific and rapid detection of enrofloxacin (ENR) in animal-derived food. The visual cut-off values were 0.1 μg L−1 ENR for CD/AgNP-based FLFIA (C-FLFIA) and 0.25 μg L−1 ENR for QD/AuNP-based FLFIA (Q-FLFIA). Meanwhile, the cut-off values were 5 μg L−1 ENR for a traditional AgNP-based lateral flow immunochromatographic assay (Ag-LFIA) and 10 μg L−1 ENR for AuNP-based LFIA (Au-LFIA). In spiked and procured animal-derived food samples (crucian, perch, pork, beef, chicken, and milk), the cut-off values were 0.5–1 μg kg −1 (μg L−1) ENR for C-FLFIA and 1.25–2.5 μg kg−1 (μg L−1) for Q-FLFIA. The cut-off values of the two assays are much lower than the maximum limits of ENR set by standardization agencies around the world.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...