Robust and highly specific fluorescence sensing of Salmonella typhimurium based on dual-functional phi29 DNA polymerase-mediated isothermal circular strand displacement polymerization
Abstract
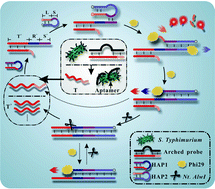
A simple and robust fluorescence sensing strategy has been developed for the detection of pathogenic bacteria by the combination of the dual functionality of phi29 DNA polymerase with isothermal circular strand displacement polymerization (ICSDP). The strategy relies on target-triggered formation of a mature primer that initiates the cyclic strand displacement polymerization reaction with the aid of dual functional phi29; thus, amplified detection of the target can be achieved. To our knowledge, this work is the first report where dual functional phi29-assisted ICSDP has been employed for fluorescence sensing of pathogenic bacteria. It is worth noting that a hairpin pre-primer is introduced that can be trimmed into a mature primer for initiating ICSDP via the 3′ → 5′ proofreading exonuclease activity of phi29, which contributes to the ultrahigh specificity of the strategy owing to the elimination of the unwished nonspecific extension. On the basis of the present amplification strategy, our biosensor exhibits excellent specificity and sensitivity toward S. typhimurium with an excellent detection limit as low as 1.5 cfu mL−1. In addition, the strategy offers the advantages of a simplified operation, shortened analysis time, and highly sensitive detection of pathogens with only a one-step reaction. Furthermore, by redesigning the corresponding binding molecules, the proposed strategy can be easily extended for the detection of a wide spectrum of analytes. Hence, the dual functional phi29-assisted ICSDP strategy indeed creates a robust and convenient fluorescence sensing platform for the identification of pathogenic bacteria and related food safety analysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...