Multi-code magnetic beads based on DNAzyme-mediated double-cycling amplification for a point-of-care assay of telomerase activity†
Abstract
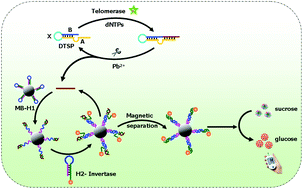
Development of a reliable and facile telomerase activity assay with high specificity and sensitivity is a central challenge to make telomerase testing a routine part of medical care with respect to cancer. Herein, we propose a point-of-care (POC) assay of telomerase activity based on multi-code magnetic beads initiated by DNAzyme-mediated double-cycling amplification coupling with a glucometer. A designed DNAzyme-based telomerase substrate prime (DTSP) probe consists of three regions (AXB) for a DNAzyme catalytic sequence, poly-thymine (poly-T) linker and telomere primer sequence. In the presence of telomerase, telomerase elongates the primer site on the DTSP probe. Subsequent addition of the PbII cofactor activates the DNAzyme, which cleaves the elongated fragment at the RNA site, and releases the DTSP probe for repetitive cycling and the elongated fragment. The cleaved fragment as a trigger then continuously triggers the cyclic strand displacement reaction (CSDR) between MB-H1 and invertase-H2, constructing the second cycling and forming the MB-H1/invertase-H2 duplex. Owing to the double-cycling amplification, numerous invertases were coded onto the surface of MBs. After magnetic separation, the enriched multi-code MB catalytically hydrolyzes the sucrose substrate with multiple turnovers, generating a large amount of glucose for quantitative readout by personal glucose meters (PGM). Benefiting from the double-cycling amplification and magnetic separation, a high signal-to-background ratio was achieved, and the point-of-care assay realizes sensitive telomerase activity detection down to 5 HeLa cells with a significantly enhanced dynamic range without the need for enzymatic amplification. The designed DTSP probe highly ensured the specificity and reliability due to the high dependence of DNAzyme on the metal ion cofactor. Moreover, this method can be applied for the screening of telomerase inhibitors and the discrimination of cancer cells from normal cells. With the ability of simple operation, outstanding sensitivity, and excellent selectivity, this method offers a convenient and specific POCT strategy for telomerase activity detection, holding great potential in clinical diagnosis and drug discovery.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Analyst Recent HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...