Infrared attenuated total reflection and 2D fluorescence spectroscopy for the discrimination of differently aggregated monoclonal antibodies†
Abstract
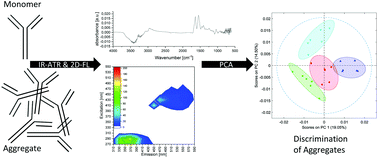
Antibody aggregates may occur as undesirable by-products during the manufacturing process of biopharmaceutical proteins since parameters such as pH, temperature, ionic strength, protein concentration, oxygen, and shear forces can lead to aggregate formation. These aggregates have to be detected, quantified and removed cost extensively, since they may reduce the safety and efficacy of the product. Protein aggregates can range from small soluble dimers up to large visible agglomerates. Differently aggregated antibody samples were characterized for their soluble and insoluble aggregate concentration by size exclusion chromatography and fluorescence microscopy, respectively. The samples exhibited a high diversity of protein aggregates, which varied in amount, size and shape. For secondary structure characterization, infrared attenuated total reflection (IR-ATR) and two-dimensional fluorescence (2D-FL) spectroscopy were applied. Using direct spectroscopy, only marginal differences of various antibody aggregates were evident. However, using appropriate chemometric strategies, the evaluation of IR-ATR and 2D-FL spectra yielded the discrimination of differently aggregated antibody samples with yet unprecedented precision.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...