Multiplexing cytokine analysis: towards reducing sample volume needs in clinical diagnostics†
Abstract
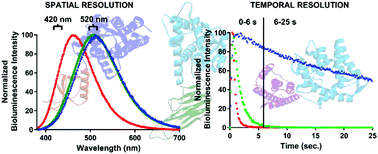
The trend for improved more precise diagnostics and management of disease heavily relies on the measurement of panels of biomarkers in physiological samples of patients. Ideally, the ultimate goal would be to detect as many clinically relevant biomarkers as possible in a single drop of blood, achieving quick, sensitive, reproducible, and affordable detection in small volume physiological samples. Bioluminescent (BL) proteins provide many of the desired characteristics required for such labels, including detection at extremely low concentrations, no interference from physiological fluids leading to excellent detection limits, and compatibility with many miniaturized systems. However, to date the use of BL proteins has been restricted by their limited multiplexing capabilities. BL proteins typically exhibit a single emission profile and decay kinetics making the simultaneous detection of multiple analytes difficult. Recent progresses in this area include the use of two different engineered luminescent proteins to achieve resolved signals via one-dimensional time resolution. This approach, however, to date only lead to a dual analyte detection. Herein, we have demonstrated that using a two-dimensional approach that combines both temporal and spatial resolution, we can expand the multiplexing capabilities of bioluminescent proteins. To that end, the photoprotein aequorin (AEQ) has been employed for the simultaneous detection of three separate analytes in a single well, differentiated through the use of three discrete time/wavelength windows. Through a combination of site-specific mutations and synthetic coelenterazines “semi-synthetic” AEQ variants have been developed with altered emission profiles and decay kinetics. In this study, two AEQ mutant proteins were genetically conjugated to three pro-inflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukins 6 and 8) resulting in AEQ-labeled cytokines. These fusion proteins were combined with synthetic coelenterazines resulting in proteins with differing emission maxima and half-lives to allow for the simultaneous detection of all three cytokines in a single sample. The validity of the assay was demonstrated in serum by employing human physiological samples and comparing our results with commercially available individual tests for each of the three cytokines.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
