Wide-range non-contact fluorescence intensity ratio thermometer based on Yb3+/Nd3+ co-doped La2O3 microcrystals operating from 290 to 1230 K†
Abstract
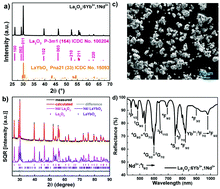
Non-contact ratiometric thermometry has applications ranging from in situ physiological measurements to industrial process monitoring. The technique is based on the optical detection of the fluorescence intensity ratio (FIR) of two thermally-coupled levels (TCLs). Here, we report a Yb3+/Nd3+ co-doped La2O3 microcrystal ratiometric thermometer based on upconverted emission in the near-infrared (NIR) after excitation with a 980 nm laser diode, which operates effectively over the wide temperature range from 290–1230 K. The thermometer uses the TCLs of Nd3+:4F7/2 (emission peak 762 nm) and Nd3+:4F5/2 (emission peak 825 nm). The chosen levels combine desirable characteristics to act as a sensitive temperature sensor over a wide range of elevated temperatures: namely a suitable energy gap (ΔE = 950 cm−1); and weak thermal quenching effects (maximum photoluminescence at 803 and 853 K respectively for two Nd3+ emission peaks). This leads to a high relative sensitivity (SR) of 1334/T2, and low temperature uncertainty ΔTmin of 0.1 K (<400 K), 1 K (400–853 K) and 3 K (853–1233 K). In addition to these characteristics, the excellent repeatability of FIR of the two Nd3+ emission peaks makes Yb3+/Nd3+ co-doped La2O3 microcrystals a promising non-contact NIR ratiometric thermometer for temperatures up to 1230 K.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...