Synthesis and characterization of a fluorinated S-nitrosothiol as the nitric oxide donor for fluoropolymer-based biomedical device applications†
Abstract
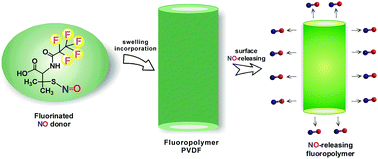
Fluorinated polymers are widely used as biomaterials in various biomedical implant and device applications. However, thrombogenicity, surface-induced inflammation, and the risk of microbial infection remain key issues that can limit their use. In this work, we describe the first nitric oxide (NO) releasing fluorinated polymer, in which a new fluorinated NO donor, S-nitroso-N-pentafluoropropionyl-penicillamine (C2F5-SNAP), is incorporated within a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) tubing. The synthesis, decomposition kinetics, and NO-release characteristics of the C2F5-SNAP species are described in detail. Then, using a simple solvent swelling method, we demonstrate that C2F5-SNAP can readily be doped into PVDF tubing. The resulting tubing can release NO for 11 days under physiological conditions, with an NO flux >0.5 × 10−10 mol cm−2 min−1 over the first 7 days. Due to fluorous–fluorous interactions, the leaching of the fluorinated NO donor and its decomposed products is shown to be very low (less than 5 nmol mg−1, total). Furthermore, the new NO-releasing PVDF tubing exhibits significant antimicrobial activity (compared to undoped PVDF tubing) against both Gram positive and negative S. aureus and P. aeruginosa bacterial strains over a 7 d test period. This new NO-releasing fluorinated polymer is likely to have the potential to improve the biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity of various biomedical devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...