An Er-doped TiO2 phase junction as an electron transport layer for efficient perovskite solar cells fabricated in air†
Abstract
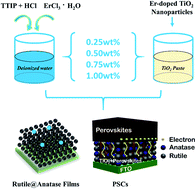
Current perovskite solar cells (PSCs) often use high-purity single-crystal metal oxides prepared by complex growth processes as electron transport layers (ETLs). In particular, TiO2, as an ETL, can deteriorate the stability of PSCs under illumination. Here, we report a passivation strategy using Er-doped TiO2 synthesized with a one-step hydrothermal method as an ETL. Notably, the oxygen-induced defects in TiO2 have decreased to an acceptable level for PSCs due to the introduction of Er3+ ions. More interestingly, we find that a phase junction can be formed in the mixed crystalline rutile/anatase phase of TiO2, and this TiO2 phase junction can achieve efficient charge separation and accelerate internal electron transfer of the ETL. Taking advantage of these facts, we obtain TiO2-based PSCs through a two-step sequential deposition method in ambient air, whose best efficiency increases by 45.8%. Moreover, the Er-doped device exhibits remarkable ultraviolet resistance ability, whose efficiency is maintained over 90% even after 500 hour ultraviolet irradiation. We believe that this demonstrated strategy provides an effective way for preparing efficient and ultraviolet resistant PSCs in air.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...