A solar rechargeable battery based on the sodium ion storage mechanism with Fe2(MoO4)3 microspheres as anode materials†
Abstract
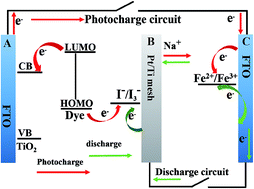
In this communication, a simple solar rechargeable battery based on the sodium ion storage mechanism with Fe2(MoO4)3 microspheres as anode materials is proposed for the first time. The battery can be photo-charged under solar irradiation, and discharged reversibly in the dark. Therefore, photon–electron conversion, and energy storage and release based on reversible sodium ion insertion and extraction can be realized in the solar rechargeable battery.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...