K2V6O16·2.7H2O nanorod cathode: an advanced intercalation system for high energy aqueous rechargeable Zn-ion batteries†
Abstract
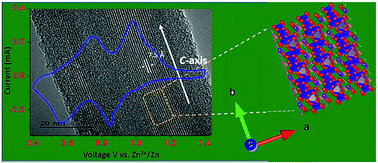
1D nanorods of the layered material K2V6O16·2.7H2O (KVO) are implemented for the first time as cathode materials in secondary aqueous rechargeable Zn-ion batteries (ARZIBs) and exhibit excellent electrochemical Zn storage properties. This cathode material delivers a reversible capacity of 296 mA h g−1 over 100 cycles. At current densities of 1000, 3000, and 5000 mA g−1 for 700 cycles, the electrode displays reversible capacities of 223, 177, and 138 mA h g−1, for approximately 170, 300, and 230 cycles, respectively. In addition to these properties, it withstands over 500 cycles at an applied current density of 6000 mA g−1 with nearly 82% capacity retention. The battery offers a specific energy of 128 Wh kg−1 at a specific power of 5760 W kg−1, revealing the advantages of the material in an eco-friendly atmosphere.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...