Infinite coordination polymer networks: metallogelation of aminopyridine conjugates and in situ silver nanoparticle formation†
Abstract
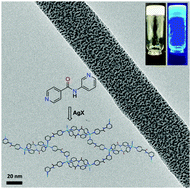
Herein we report silver(I) directed infinite coordination polymer network (ICPN) induced self-assembly of low molecular weight organic ligands leading to metallogelation. Structurally simple ligands are derived from 3-aminopyridine and 4-aminopyridine conjugates which are composed of either pyridine or 2,2′-bipyridine cores. The cation specific gelation was found to be independent of the counter anion, leading to highly entangled fibrillar networks facilitating the immobilization of solvent molecules. Rheological studies revealed that the elastic storage modulus (G′) of a given gelator molecule is counter anion dependent. The metallogels derived from ligands containing a bipyridine core displayed higher G′ values than those with a pyridine core. Furthermore, using single crystal X-ray diffraction studies and 1H–15N two-dimensional (2D) correlation NMR spectroscopy, we show that the tetracoordination of silver ions enables simultaneous coordination polymerization and metallosupramolecular cross-linking. The resulting metallogels show spontaneous, in situ nanoparticle (d < 2–3 nm) formation without any additional reducing agents. The silver nanoparticle formation was followed using spectroscopic studies, and the self-assembled fibrillar networks were imaged using transmission electron microscopy (TEM) imaging.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...