Charge regulating macro-ions in salt solutions: screening properties and electrostatic interactions
Abstract
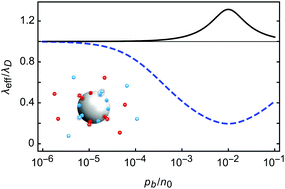
We revisit the charge-regulation mechanism of macro-ions and apply it to mobile macro-ions in a bathing salt solution. In particular, we examine the effects of correlation between various adsorption/desorption sites and analyze the collective behavior in terms of the solution effective screening properties. We show that such a behavior can be quantified in terms of the charge asymmetry of the macro-ions, defined by their preference for a non-zero effective charge, and their donor/acceptor propensity for exchanging salt ions with the bathing solution. Asymmetric macro-ions tend to increase the screening, while symmetric macro-ions can in some cases decrease it. Macro-ions that are classified as donors display a rather regular behavior, while those that behave as acceptors exhibit an anomalous non-monotonic Debye length. The screening properties, in their turn, engender important modifications to the disjoining pressure between two charged surfaces. Our findings are in particular relevant for solutions of proteins, whose exposed amino acids can undergo charge dissociation/association processes to/from the bathing solution, and can be considered as a solution of charged regulated macro-ions, as analyzed here.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Electrostatics and Soft Matter


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...