Analysis of network formation and long-term stability in silica nanoparticle stabilized emulsions†
Abstract
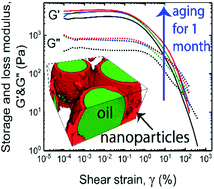
Emulsions are widely used in industrial applications, including in food sciences, cosmetics, and enhanced oil recovery. For these industries, an in depth understanding of the stability and rheological properties of emulsions under both static and dynamic conditions is vital to their successful application. Presented here is a thorough assessment of a model nanoparticle (NP) stabilized dodecane-in-water emulsion as a route to improved understanding of the relationship between NP properties, microstructure and droplet–droplet interactions on the stability and rheological properties of emulsions. Emulsions are obtained here with low NP loadings without the need for added electrolyte through the use of an optimized silica NP (SNP) surface modification procedure. The prepared emulsions were characterized via optical microscopy, cryo-scanning electron microscopy (cryo-SEM), zeta potential analysis and laser scanning confocal microscopy (LSCM), enabling quantification of the emulsion droplet size, SNP interfacial coverage/morphology and surface charge. The correlation of these properties with the rheology of the emulsions is investigated through small amplitude oscillatory shear experiments which provide significant insight into the origins of the emulsions’ rheological behavior and their stability. In addition, long-term stability, droplet–droplet network formation and microstructural evolution are found to be readily detectable shortly after preparation through measured progression of the emulsion's rheological properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...