Two-dimensional Fe3O4/MoS2 nanocomposites for a magnetorheological fluid with enhanced sedimentation stability†
Abstract
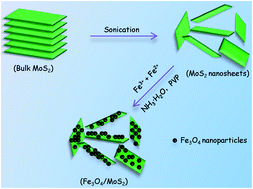
Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles were successfully deposited on the surface of MoS2 nanosheets (Fe3O4/MoS2) by a sonochemical method and the obtained Fe3O4/MoS2 nanocomposites were used as a promising candidate for a magnetorheological (MR) fluid. This MR fluid was prepared from the Fe3O4/MoS2 nanocomposites and its corresponding MR performances were examined using a rotational rheometer. The MR fluid based on Fe3O4/MoS2 showed typical MR effects with increasing viscosity, shear stress, yield stress and dynamic shear modulus depending on the applied magnetic fields. Compared with commercial carbonyl iron (CI) particles, the sedimentation stability of the Fe3O4/MoS2–MR fluid was greatly improved because of its unique two-dimensional structure and the reduced fluid–particle density mismatch. Therefore, the prepared Fe3O4/MoS2-based MR fluid with typical MR effects and good sedimentation stability would have great potential in practical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...