Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleConfining the polymerization degree of graphitic carbon nitride in porous zeolite-Y and its luminescence
Wei Wan,
Jia-Yi Sun,
Shi Ye * and
Qin-yuan Zhang
* and
Qin-yuan Zhang *
*
State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Fiber Laser Materials and Applied Techniques, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510641, China. E-mail: msyes@scut.edu.cn; qyzhang@scut.edu.cn
First published on 12th July 2018
Abstract
Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) has aroused broad interest in the field of photocatalysis and luminescence as a kind of metal-free semiconductor with a suitable band gap of ∼2.7 eV. The properties largely depend on the polymerization degree of g-C3N4. This research exploits the nanocages of zeolite-Y to confine the polymerization of the melamine monomer to form g-C3N4. The composites are achieved via a facile two-step method, i.e., melamine–Na+ ion exchange reaction in the cage of the zeolite and subsequent calcination. BET measurement and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) confirm that the g-C3N4 is encapsulated in zeolite-Y, and the polymerization degree can be controlled by the melamine contents exchanged with Na+ in the cages of zeolite-Y. Photoluminescence and vibration spectroscopy also show the features of g-C3N4 with different polymerization degrees in the zeolite-Y composites. This research gives a perspective of fabricating subnanoscale g-C3N4 in porous zeolite, which may find potential applications in photocatalysis and optoelectronics.
1. Introduction
As a kind of carbon nitride allotrope, graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) is composed of heptazine tectonic units and pendant amino groups. Benefitting from its special layer structure and electronic structure, g-C3N4 has become a novel organic and metal-free semiconductor with outstanding heat endurance and chemical resistance in the ambient environment.1 Owing to the suitable band gap of 2.7 eV, g-C3N4 also exhibits excellent photocatalytic properties under irradiation with visible light, including photo-degradation, photocatalytic NO removal and photocatalytic water splitting.2–18 Various synthetic methods and techniques, such as solvothermal synthesis, physical vapor deposition, chemical vapor deposition, thermal nitridation, etc., have been employed to produce g-C3N4. Additionally, a moderate approach ensuring the thermal condensation of simple organic monomers like melamine was reported to synthesize g-C3N4 as a low cost and simple synthetic method.19 Distinct photoluminescence (PL) properties can be acquired for the g-C3N4 with varied polymerization degrees, which was achieved via condensation of melamine at different synthetic temperature.19,20 With the ongoing condensation of melamine monomers, melon is the first formed polymeric C3N4 structure as an important intermediate precursor. Further reaction results in more polymerized and less defective g-C3N4.21,22 Thus, controlling the condensation of melamine is of significance. Differing from changing the synthetic temperature, we report on a new method to control the polymerization of g-C3N4 by utilizing the confining effect of zeolite-Y's pores, which has not yet been reported to our best knowledge.Zeolite-Y is builded up by [AlO4]5− and [SiO4]4− tetrahedra constituting an open 3D framework structure with cages and channels, which could accommodate particles smaller than 1.5 nm.23–26 It also can be viewed as silica structure with partial [SiO4]4− units substituted by [AlO4]5−, resulting in a negative charge of the structure stabilized by positive cations in the cages and channels.27 Zeolite-Y has been regarded as an outstanding host to encapsulate quantum dots (QDs) luminescent center, for preventing the QDs from attack of moisture, etc.28–33 Many approaches, including ion exchange, vapor impregnation and solid state diffusion, can be employed to introduce luminescent centers into the cages of zeolite-Y.34 Accordingly, the cations in the cages of zeolite-Y are supposed to be exchanged by the cationic amine, which would further condense to produce g-C3N4. Thus, utilizing the cages of zeolite-Y could be a feasible way to confine the polymerization of g-C3N4, which may find potential applications in photocatalysis, lighting device and chemical sensing, etc.
In this research, we report on a facile synthesis of porous zeolite-Y and g-C3N4 composites, aiming to confine the polymerization of g-C3N4 and tune the resulted luminescence. We successfully synthesized the zeolite-Y and g-C3N4 composites by two steps. Melamine is first dissolved in deionized water and introduced into the pores of zeolite-Y as precursor via an ion-exchange reaction. Through the thermal condensation of melamine in the second step, we eventually synthesized the zeolite-Y and g-C3N4 composites.
2. Experimental section
Materials and chemicals: Melamine powders (Aladdin, 99%) and Na+–zeolite-Y (SiO2/Al2O3 = 5.1, Alfa Aesar).The zeolite-Y and g-C3N4 composites (simplified as CNr–Y, r refers to the initial mass of melamine dissolved in 50 mL deionized water), were generally synthesized by two steps. Typically, the melamine exchanged zeolite-Y was firstly prepared. Detailedly, the amount of r g (r = 1.2, 1.4 or 2.0) of melamine powders were stirred and dissolved in 50 mL deionized water in a water bath at 80 °C for 0.5 h. Then 1.0 g of zeolite-Y was added in melamine solution and magnetically stirred in a water bath at 80 °C for 48 h. The melamine-ion was introduced into the pores of zeolite-Y via the ion-exchange reaction. The as-prepared precursors were repeatedly centrifuged and then washed with deionized water (for twice), and finally dried in air at 80 °C for 12 h. In a second step, the as-prepared precursors were calcined at 550 °C under N2 atmosphere for 3 h. The CNr–Y products were used directly for further investigation.
Bulk g-C3N4 was synthesized by direct heating 2 g of melamine powders at 550 °C under N2 atmosphere for 3 h.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the samples were measured on a Rigaku D/max-IIIA X-ray diffractometer using Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.5418 Å). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images were obtained using an FEI Nova Nano SEM 430 field-emission scanning electron microscopy. The transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images and elemental mapping of resin-embedded sections of CNr–Y were recorded on a JEOL JEM-2100F transmission electron microscope. The specific surface area of the samples was checked by BET measurement (Quantachrome Autosorb-iQ). PL and excitation spectra were recorded on an Edinburgh Instruments FLS 920 spectrometer with a red-sensitive photomultiplier tube (R928). Fluorescence lifetimes were measured on a Hamamatsu Photonics C11367-11. Raman scattering spectroscopy measurements were carried out with 785 nm excitation using a micro-Raman spectroscopy (HORIBA JOBIN YVON LabRAM Aramis). Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was carried out on Thermo Fisher NICOLET IS 50.
3. Results and discussion
3.1 Synthesis, structure and morphology
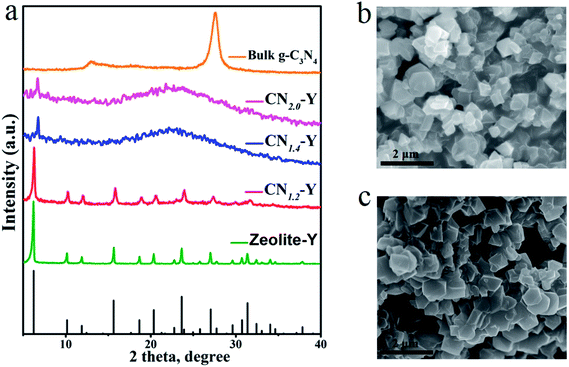
Fig. 1 depicts the schematic synthetic procedure of CNr–Y. Fig. 2a shows XRD patterns of the bulk g-C3N4, the raw zeolite-Y and CNr–Y (r = 1.2, 1.4, 2.0), respectively. For the pattern of bulk g-C3N4 (orange), two major peaks at around 12.9° and 27.6° are assigned to the in-plane structure packing of aromatic systems of (100) plane and the interlayer stacking of conjugated aromatic systems of (002) plane, respectively, indicating that it is the typical graphite phase.21,35–38 It can be seen that both the patterns of CN1.2–Y (red) and raw zeolite-Y (olive) are in good agreement with reference pattern (black bar), which suggests that the porous zeolite framework is maintained for CN1.2–Y. Differently, the CNr–Y (r = 1.4 and 2.0) are almost amorphous with only one declined diffraction peak at around 6.7°, which show slightly shift to higher diffraction angle compared to that of the raw zeolite-Y. It is the typical fingerprint of zeolite-Y with microporous structure, suggesting that the framework of the CNr–Y (r = 1.4 and 2.0) do not totally collapse.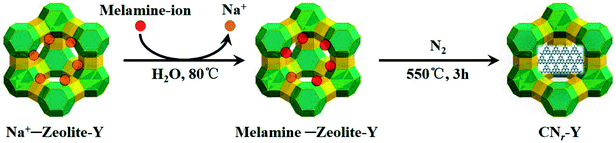 | ||
| Fig. 1 Schematic illustration of the two-step synthesis of CNr–Y, involving melamine-ion exchange followed by calcination. | ||
Fig. 2b and c depict the SEM images of CN1.2–Y and raw zeolite-Y, respectively. Obviously, the particles of the CN1.2–Y are angular with similar morphology and smooth surfaces compared to that of the raw zeolite-Y, suggesting that the exchanged melamine may take reaction inside the pores of zeolite-Y during calcination.27,28
Fig. 3a is the adsorption–desorption isotherms of some typical samples. The adsorption–desorption behavior of each sample exhibits the typical porous feature. The maximum adsorption capacity of the raw zeolite-Y is 215.83 g cm−3, while that of CN1.2–Y and CN1.4–Y are 179.48 g cm−3 and 74.73 g cm−3, respectively. The specific surface area of these samples in Fig. 3b shows analogous tendency, suggesting that the melamine derived products are indeed encapsulated in cages of zeolite-Y, and higher melamine contents result in more filled structure of the porous zeolites.27 Further evidences by elemental mapping will be given in Fig. 4.
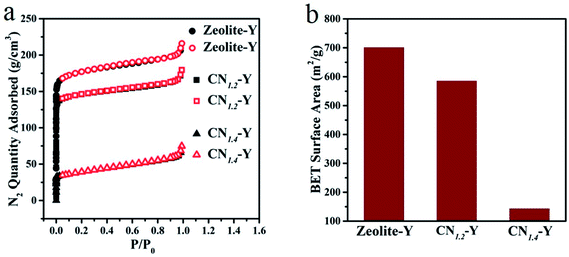 | ||
| Fig. 3 (a and b) N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms and specific surface area of the CN1.2–Y, CN1.4–Y and the raw zeolite-Y. | ||
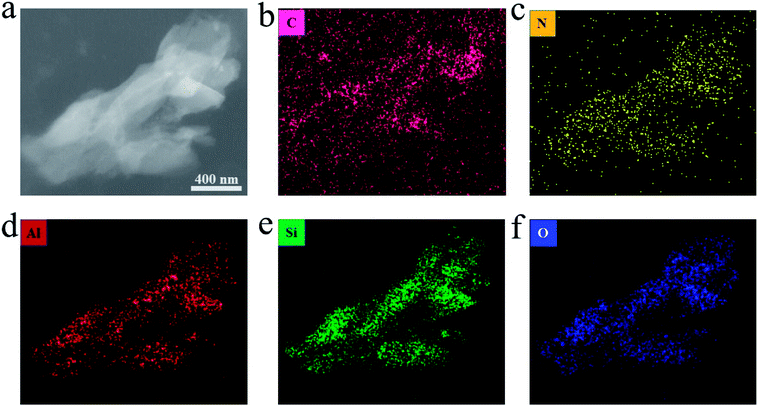 | ||
| Fig. 4 (a) TEM image of the CN1.2–Y. (b–f) The elemental mapping of C, N, Al, Si and O in the same particles. | ||
Fig. 4a is a TEM image of resin-embedded section of CN1.2–Y sample and the respective compositional elemental mapping images are shown in Fig. 4(b–f). It is worth noting that the homogeneous distribution of nitrogen element in the particles (broken pieces of a zeolite grain), as seen in Fig. 4c, which is a direct evidence for the supposedly formed C3N4 encapsulated in the pores of zeolite-Y. Although the carbon element seems to be everywhere owing to the resin package, more carbon contents are found in the particles than that in the resin. The aluminum element, silicon element and oxygen element distribution share the same shapes, which are the profiles of zeolite-Y pieces.23 Considering the negative charged framework of the zeolite and the feature of ion exchange reaction, there should be electrostatic interaction between the zeolite-Y and g-C3N4.
3.2 Photoluminescence properties
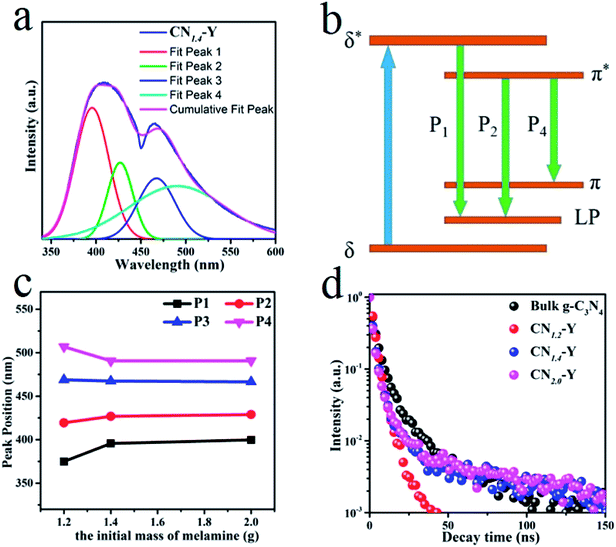
The normalized emission spectra of bulk g-C3N4 and all CNr–Y (r = 1.2, 1.4, 2.0) samples are shown in Fig. 5a. All the CNr–Y (r = 1.2, 1.4, 2.0) samples apparently show two emission peaks with similar profiles, and the dominant emission peak of bulk g-C3N4 locates at around 456 nm under the excitation of 320 nm. The dominant emission peaks of the CNr–Y (r = 1.2, 1.4, 2.0) are located at around 386, 410, and 407 nm, respectively, which are analogous with the previous reports on the different polymerization of g-C3N4 synthesized at various temperature.19,20 It is the direct evidence for the existence of g-C3N4 in the composites. The emissions of the CNr–Y samples clearly show blue shift in contrast with bulk g-C3N4. Detailedly, the emission of CNr–Y exhibits red shift in the sequence of r = 1.2, 1.4, 2.0, which is owed to the different polymerization degrees of g-C3N4. This is ascribed to the encapsulation of g-C3N4 in the cages of zeolite-Y with diameter of subnanoscale, resulting in a quantum confinement effect on the electronic structure of the encapsulated g-C3N4.24–26,39,40 Accordingly, all the excitation spectra in Fig. 5b show similar trend.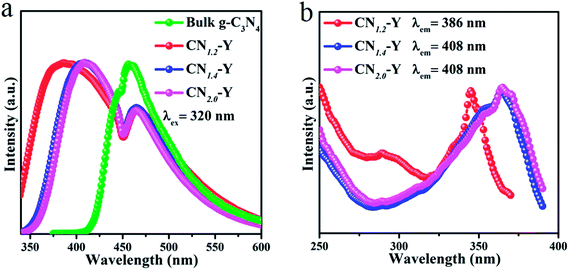 | ||
| Fig. 5 (a) The normalized PL emission spectra of the CNr–Y (r = 1.2, 1.4, 2.0) and bulk g-C3N4. (b) The normalized excitation spectra of the CNr–Y (r = 1.2, 1.4, 2.0). | ||
With the help of Gaussian fitting of the PL peaks, we could obtain a clear understanding of these peaks. The fitted results of the CN1.4–Y sample are depicted in Fig. 6a. It can be seen that the PL spectrum of CN1.4–Y sample has four emission peaks centered at P1 (396 nm), P2 (427 nm), P3 (467 nm) and P4 (491 nm), respectively. According to the previous research on g-C3N4,19,41,42 the band-gap states of g-C3N4 are comprised of a sp2 C–N σ band, sp3 C–N π band and the lone pair (LP) state of the bridge nitride atom (Fig. 6b). The P1, P2, and P4 originate from the different transitions: σ*–LP, π*–LP and π*–π, respectively. The fitting peak positions of CNr–Y are depicted in Fig. 6c. The red shift of P1 and P2 reflects the extension of the encapsulated g-C3N4 network, proving that the subnanocages of zeolite-Y can control the polymerization degree of g-C3N4. It is strongly evidenced by the emission blue shift of CN1.2–Y compared with that of CNr–Y (r = 1.4 or 2.0).19,20 According to Füle et al., the size of the sp2 carbonic clusters should be within the range of 0.94–1.15 nm in order to enable the direction transition between the π and π* bands.38,41,43 The appearance of the π*–π transition bands of CNr–Y (r = 1.2, 1.4, 2.0) samples, corresponding to the peak P4, directly proves that g-C3N4 is encapsulated in the pores of zeolite-Y with a diameter of subnanoscale. The peak position of P3 remains at around 467 nm, which is probably due to the presence of NH2 on the edge and the defect of C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N.38 It can be further proved in the FTIR spectroscopy.
N.38 It can be further proved in the FTIR spectroscopy.
The PL decay curves of the bulk g-C3N4 and CNr–Y (r = 1.2, 1.4, 2.0) are presented in Fig. 6d, which are all monitored at their dominant emission peaks under the 320 nm excitation. All the samples show a fast decay component of 1.7–3.1 ns, which indicates that they share the same origin of σ*–LP. While the samples other than CN1.2–Y exhibit a more complicated long decay, suggesting that a multiple process such as charge-carrier trapping may be involved for these higher polymerized samples.19,44
Low temperature PL measurements of the CN1.2–Y, CN1.4–Y and bulk g-C3N4 were carried out and the results are given in Fig. 7a, b and c, respectively. All their emissions are gradually enhanced with the decline of temperatures. While the peak locations and profiles remain unchanged for CN1.4–Y and bulk g-C3N4 as the temperature decreases. Differing from this phenomenon, the edge at short wavelength shows red shift for CN1.2–Y as the temperature decreases, which could ascribed to the lower polymerization degree of g-C3N4 for CN1.2–Y than that of CN1.4–Y and bulk g-C3N4.
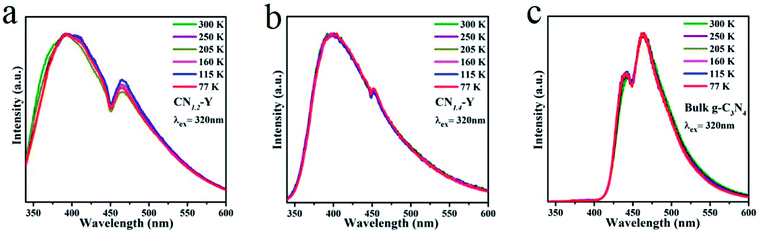 | ||
| Fig. 7 (a–c) The normalized PL emission spectra of the CN1.2–Y, CN1.4–Y and bulk g-C3N4 at various temperatures. | ||
3.3 Raman spectroscopy and FTIR spectroscopy
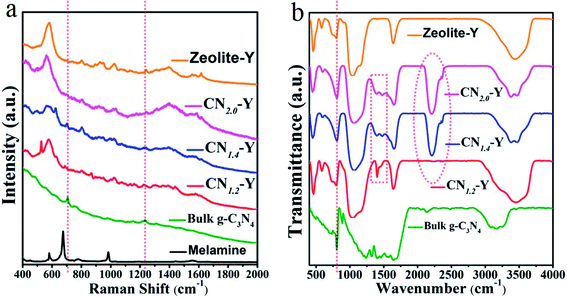
To further identify the composition of the composites, Raman spectroscopy of the raw zeolite-Y, melamine, bulk g-C3N4 and all CNr–Y (r = 1.2, 1.4, 2.0) samples were recorded and the results are presented in Fig. 8a. Typical Raman peaks of bulk g-C3N4 locate at around 707 and 1233 cm−1, which are induced by the heptazine ring breathing mode and stretching vibration modes of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N and C–N hetero-cycles, respectively. These features indicate the formation of graphite structure in bulk g-C3N4.20,45,46 The melamine has two fingerprint peaks located at around 675 cm−1 (triazine ring breathing mode) and 1558 cm−1 (NH2 bending mode), respectively.47,48 These two peaks disappear for the CNr–Y (r = 1.2, 1.4, 2.0) samples, implying that the melamine has been finished after the polymerization reaction. Removing the Raman peaks of zeolite-Y, it could be seen that CNr-Y (r = 1.2, 1.4, 2.0) samples have a tiny Raman peaks at around 707 cm−1, suggesting the existence of g-C3N4 in the composites.
N and C–N hetero-cycles, respectively. These features indicate the formation of graphite structure in bulk g-C3N4.20,45,46 The melamine has two fingerprint peaks located at around 675 cm−1 (triazine ring breathing mode) and 1558 cm−1 (NH2 bending mode), respectively.47,48 These two peaks disappear for the CNr–Y (r = 1.2, 1.4, 2.0) samples, implying that the melamine has been finished after the polymerization reaction. Removing the Raman peaks of zeolite-Y, it could be seen that CNr-Y (r = 1.2, 1.4, 2.0) samples have a tiny Raman peaks at around 707 cm−1, suggesting the existence of g-C3N4 in the composites.
The FTIR spectra of all samples including the raw zeolite-Y, CNr–Y (r = 1.2, 1.4, 2.0) and bulk g-C3N4 are shown in Fig. 8b. For g-C3N4, the peaks at around 805 cm−1 are assigned to the characteristic breathing mode of the tri-s-triazine units.49 While it superposes the peaks originated from zeolite-Y. The peaks in the 1000–1700 cm−1 region are assigned to the typical stretching modes and rotation vibration of C–N and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N hetero-cycles in the network.21 The appearance of these peaks for CNr–Y (r = 1.2, 1.4, 2.0) samples evidently indicate the formation of g-C3N4 in the cages of zeolite-Y. Apparently, these peaks are strong for bulk g-C3N4. While for the CNr–Y, the interaction of laser beam with CNr is much weaker when taking the FTIR measurement since the CNr is embedded inside the zeolite, resulting in the much weaker peaks. Moreover, there are a broad bands located in the range of 3000–3400 cm−1 region, which are assigned to the absorbed H2O molecules and uncondensed amine groups including the stretching and deformation modes of –NH2 groups.50–53
N hetero-cycles in the network.21 The appearance of these peaks for CNr–Y (r = 1.2, 1.4, 2.0) samples evidently indicate the formation of g-C3N4 in the cages of zeolite-Y. Apparently, these peaks are strong for bulk g-C3N4. While for the CNr–Y, the interaction of laser beam with CNr is much weaker when taking the FTIR measurement since the CNr is embedded inside the zeolite, resulting in the much weaker peaks. Moreover, there are a broad bands located in the range of 3000–3400 cm−1 region, which are assigned to the absorbed H2O molecules and uncondensed amine groups including the stretching and deformation modes of –NH2 groups.50–53
Removing the FTIR peaks of zeolite-Y, it can be seen that there is another significant peak appearing at around 2206 cm−1 for each CNr–Y (r = 1.4 or 2.0) sample, which implies the existence of nitrile group (C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N) and other similar species. And the existence of C
N) and other similar species. And the existence of C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N in the samples is associated with drastic reactions at high temperature, resulted from the fracture of tri-s-triazine rings probably caused by the exothermic reaction of polymerization for the more concentrated melamine in CNr–Y (r = 1.4 or 2.0).38,54 The peak is absent for CN1.2–Y, manifesting that few C
N in the samples is associated with drastic reactions at high temperature, resulted from the fracture of tri-s-triazine rings probably caused by the exothermic reaction of polymerization for the more concentrated melamine in CNr–Y (r = 1.4 or 2.0).38,54 The peak is absent for CN1.2–Y, manifesting that few C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N is observed. It is probably due to that the exothermic reaction is not that drastic for the less concentrated melamine in the cage of the zeolite. It is also evidenced by the crystal feature of CN1.2–Y and the amorphous feature of CNr–Y (r = 1.4 or 2.0) in Fig. 2. Since zeolite-encapsulated particles are in a subnanoscale,23–26 it is reasonable to infer that the confining effect on condensation degree of melamine by the pores of zeolite-Y would result in a lot of –NH2 groups and C
N is observed. It is probably due to that the exothermic reaction is not that drastic for the less concentrated melamine in the cage of the zeolite. It is also evidenced by the crystal feature of CN1.2–Y and the amorphous feature of CNr–Y (r = 1.4 or 2.0) in Fig. 2. Since zeolite-encapsulated particles are in a subnanoscale,23–26 it is reasonable to infer that the confining effect on condensation degree of melamine by the pores of zeolite-Y would result in a lot of –NH2 groups and C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N as defects existing in the edge of the g-C3N4 network. The defects cause the appearance of P3 in the PL peaks for CNr–Y (r = 1.2, 1.4, 2.0), again proving that the g-C3N4 are encapsulated in the pores of zeolite-Y.
N as defects existing in the edge of the g-C3N4 network. The defects cause the appearance of P3 in the PL peaks for CNr–Y (r = 1.2, 1.4, 2.0), again proving that the g-C3N4 are encapsulated in the pores of zeolite-Y.
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, we successfully synthesized the porous zeolite-Y and graphitic carbon nitride composites via a facile two-step method. Firstly, we introduce melamine into the pores of zeolite-Y via ion-exchange reaction and the resulted products are the precursors for next step. Secondly, the aimed CNr–Y products are synthesized in situ via the thermal condensation of melamine. Various characterizations, including the PL spectroscopy, evidence the formation of the g-C3N4 encapsulated in the pores of zeolite-Y. Owing to the confining effect of the subnanoscale cages in zeolite-Y, the CNr–Y with controlled polymerization degree of the encapsulated g-C3N4 can be gained. The dimension of the polymeric network of the g-C3N4 in the composites extends and results in red shifting of PL peak as the content of the melamine monomers is elevated. The research gives new clues to fabricate organic semiconductors with different polymerization degree in a porous zeolite, which may be intriguing in photocatalysis and optoelectronics.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work is jointly supported by the NSFC (Grant No. 51772104), Local Innovative and Research Teams Project of Guangdong Pearl River Talents Program (2017Bt01X137), the Tip-top Scientific and Technical Innovative Youth Talents of Guangdong Special Support Program (2016TQ03C100), and the Guangdong Natural Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholars (2014A030306009).References
- E. G. Gillan, Chem. Mater., 2000, 12, 3906–3912 CrossRef.
- J. Liu, Y. Liu, N. Liu, Y. Han, X. Zhang, H. Huang, Y. Lifshitz, S. T. Lee, J. Zhong and Z. Kang, Science, 2015, 347, 970–974 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. Maeda, X. Wang, Y. Nishihara, D. Lu, M. Antonietti and K. Domen, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113, 4940–4947 CrossRef.
- X. Wang, K. Maeda, A. Thomas, K. Takanabe, G. Xin, J. M. Carlsson, K. Domen and M. Antonietti, Nat. Mater., 2009, 8, 76–80 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Wang, X. Wang and M. Antonietti, Angew. Chem., 2012, 51, 68–89 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. C. Yan, Z. S. Li and Z. G. Zou, Langmuir, 2010, 26, 3894–3901 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Xiong, H. Wang, Y. Zhou, Y. Sun, W. Cen, H. Huang, Y. Zhang and F. Dong, Nanoscale, 2018, 10, 8066–8074 RSC.
- X. a. Dong, J. Li, Q. Xing, Y. Zhou, H. Huang and F. Dong, Appl. Catal., B, 2018, 232, 69–76 CrossRef.
- P. Chen, F. Dong, M. Ran and J. Li, Chin. J. Catal., 2018, 39, 619–629 CrossRef.
- X. Zou and Y. Zhang, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 5148–5180 RSC.
- G. Liu, P. Niu, C. Sun, S. C. Smith, Z. Chen, G. Q. Lu and H. M. Cheng, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 11642–11648 CrossRef PubMed.
- Q. Xiang, J. Yu and M. Jaroniec, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115, 7355–7363 CrossRef.
- S. C. Yan, Z. S. Li and Z. G. Zou, Langmuir, 2009, 25, 10397–10401 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Niu, L. Zhang, G. Liu and H.-M. Cheng, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2012, 22, 4763–4770 CrossRef.
- W. J. Ong, L. L. Tan, Y. H. Ng, S. T. Yong and S. P. Chai, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 7159–7329 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Zheng, Y. Jiao, J. Chen, J. Liu, J. Liang, A. Du, W. Zhang, Z. Zhu, S. C. Smith, M. Jaroniec, G. Q. Lu and S. Z. Qiao, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 20116–20119 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Chen, J. Zhang, X. Fu, M. Antonietti and X. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 11658–11659 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. Pan, J. Xu, Y. Wang, D. Li and Y. Zhu, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2012, 22, 1518–1524 CrossRef.
- Y. Zhang, Q. Pan, G. Chai, M. Liang, G. Dong, Q. Zhang and J. Qiu, Sci. Rep., 2013, 3, 1943 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Yuan, L. Zhang, J. Xing, M. I. Utama, X. Lu, K. Du, Y. Li, X. Hu, S. Wang, A. Genc, R. Dunin-Borkowski, J. Arbiol and Q. Xiong, Nanoscale, 2015, 7, 12343–12350 RSC.
- B. Jurgens, E. Irran, J. Senker, P. Kroll, H. Muller and W. Schnick, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 10288–10300 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Xu, Y. Li, S. Peng, G. Lu and S. Li, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013, 15, 7657–7665 RSC.
- Y. Li and J. Yu, Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, 7268–7316 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. S. Kim, M. H. Lee, N. C. Jeong, S. M. Lee, B. K. Rhee and K. B. Yoon, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 15070–15071 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. S. Kim, N. C. Jeong and K. B. Yoon, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 1642–1645 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. S. Kim, N. C. Jeong and K. B. Yoon, Langmuir, 2011, 27, 14678–14688 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Ye, J. Sun, X. Yi, Y. Wang and Q. Zhang, Sci. Rep., 2017, 7, 46219 CrossRef PubMed.
- J.-Y. Sun, F. T. Rabouw, X.-F. Yang, X.-Y. Huang, X.-P. Jing, S. Ye and Q.-Y. Zhang, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27, 1704371 CrossRef.
- H. Li, H. Zhang, L. Wang, D. Mu, S. Qi, X. Hu, L. Zhang and J. Yuan, Journal of Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, 9338 RSC.
- Z. Bai, M. Fujii, K. Imakita and S. Hayashi, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2013, 173, 43–46 CrossRef.
- K. Moller, M. M. Eddy, G. D. Stucky, N. Herron and T. Bein, ChemInform, 1989, 20, 2564–2571 CrossRef.
- H. T. Sun, A. Hosokawa, Y. Miwa, F. Shimaoka, M. Fujii, M. Mizuhata, S. Hayashi and S. Deki, Adv. Mater., 2009, 21, 3694–3698 CrossRef.
- A. Corma, U. Díaz, B. Ferrer, V. Fornés, M. S. Galletero and H. García, Chem. Mater., 2004, 16, 1170–1176 CrossRef.
- G. A. Ozin, Adv. Mater., 1992, 4, 612–649 CrossRef.
- Q. Guo, Y. Xie, X. Wang, S. Lv, T. Hou and X. Liu, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2003, 380, 84–87 CrossRef.
- A. Thomas, A. Fischer, F. Goettmann, M. Antonietti, J.-O. Müller, R. Schlögl and J. M. Carlsson, Journal of Mater. Chem., 2008, 18, 4893 RSC.
- H. A. Ma, X. P. Jia, L. X. Chen, P. W. Zhu, W. L. Guo, X. B. Guo, Y. D. Wang, S. Q. Li, G. T. Zou and G. Zhang, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2002, 14, 11269 CrossRef.
- J. Yang, X. Wu, X. Li, Y. Liu, M. Gao, X. Liu, L. Kong and S. Yang, Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Process., 2011, 105, 161 CrossRef.
- X. Zhang, X. Xie, H. Wang, J. Zhang, B. Pan and Y. Xie, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 18–21 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Groenewolt and M. Antonietti, Adv. Mater., 2005, 17, 1789–1792 CrossRef.
- B. B. Wang, Q. J. Cheng, L. H. Wang, K. Zheng and K. Ostrikov, Carbon, 2012, 50, 3561–3571 CrossRef.
- B. B. Wang, Q. J. Cheng, Y. A. Chen and K. Ostrikov, J. Appl. Phys., 2011, 110, 489 Search PubMed.
- M. Füle, J. Budai, S. Tóth, M. Veres and M. Koós, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2006, 352, 1340–1343 CrossRef.
- X. Liu, S. Ye, G. Dong, Y. Qiao, J. Ruan, Y. Zhuang, Q. Zhang, G. Lin, D. Chen and J. Qiu, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2009, 42, 215409 CrossRef.
- S. Tonda, S. Kumar, S. Kandula and V. Shanker, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2, 6772 RSC.
- Q. Guo, Y. Zhang, H. S. Zhang, Y. Liu, Y. J. Zhao, J. Qiu and G. Dong, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27, 1703711 CrossRef.
- P. V. Zinin, L. C. Ming, S. K. Sharma, V. N. Khabashesku, X. Liu, S. Hong, S. Endo and T. Acosta, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2009, 472, 69–73 CrossRef.
- R. J. Meier, J. R. Maple, M. J. Hwang and A. T. Hagler, J. Phys. Chem., 1995, 99, 5445–5456 CrossRef.
- J. Wei, P. Hing and Z. Q. Mo, Surf. Interface Anal., 2015, 28, 208–211 CrossRef.
- J. R. Holst and E. G. Gillan, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 7373–7379 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. J. Bojdys, J. O. Müller, M. Antonietti and A. Thomas, Chemistry, 2008, 14, 8177–8182 CrossRef PubMed.
- S.-W. Bian, Z. Ma and W.-G. Song, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113, 8668–8672 CrossRef.
- Y. Cui, J. Zhang, G. Zhang, J. Huang, P. Liu, M. Antonietti and X. Wang, Journal of Mater. Chem., 2011, 21, 13032 RSC.
- J. Li, C. Cao, J. Hao, H. Qiu, Y. Xu and H. Zhu, Diamond Relat. Mater., 2006, 15, 1593–1600 CrossRef.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 |