Open Access Article
Open Access Article1,2,3-Triazole-fused spirochromenes as potential anti-tubercular agents: synthesis and biological evaluation†
Dongamanti Ashok *a,
Pamula Chiranjeevia,
Aamate Vikas Kumara,
Madderla Sarasijab,
Vagolu Siva Krishnac,
Dharmarajan Sriramc and
Sridhar Balasubramaniand
*a,
Pamula Chiranjeevia,
Aamate Vikas Kumara,
Madderla Sarasijab,
Vagolu Siva Krishnac,
Dharmarajan Sriramc and
Sridhar Balasubramaniand
aGreen and Medicinal Chemistry Lab, Department of Chemistry, Osmania University, Hyderabad-500 007, Telangana State, India. E-mail: ashokdou@gmail.com
bDepartment of Chemistry, Satavahana University, Karimnagar-505001, Telangana State, India
cDepartment of Pharmacy, Birla Institute of Technology & Science – Pilani, Hyderabad Campus, Jawahar Nagar, Hyderabad-500 078, Telangana State, India
dX-ray Crystallography Division, CSIR-Indian Institute of Chemical Technology, Hyderabad-500 007, India
First published on 9th May 2018
Abstract
A facile and convenient approach has been designed for the synthesis of novel prototypes that possess the advantage of the two pharmacophores of chromene and 1,2,3-triazole in a single molecular backbone, were evaluated against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv strain. The new analogues 1,2,3-triazole-fused spirochromenes were accomplished in four step synthetic strategy utilizing click chemistry ([3 + 2] Huisgen cycloaddition) in the ultimate step. The synthesized compounds were established based on the spectral data and X-ray crystal structure for 7a. Among the compounds tested against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv strain, some products exhibited potent antimycobacterial activity with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values ranging from 1.56 to 6.25 μg mL−1. Compounds exhibiting good in vitro potency in the MTB MIC assay were further examined for cytotoxicity in a RAW 264.7 cells. Compounds 7a, 7d, 7i (MIC: 1.56 μg mL−1) and 7k, 7m (MIC: 3.125 μg mL−1) exhibited promising hits.
Introduction
Tuberculosis, the world's most chronic infectious disease caused by single infectious agent Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB), claimed the lives of over 1.3 million people worldwide in 2016, which ranks above HIV/AIDS.1 The current therapy of TB with first-line and second-line drugs are around 50 years old and moreover, it requires longer duration for the treatment.2 Patients often fail to complete the therapy due to drug side effects and the complexity of the drug regimen, leading to the emergence of multidrug resistant TB (MDR-TB), extensively drug resistant TB (XDR-TB) and totally drug resistant TB (TDR-TB).3 Additionally, the resurgence in TB is alarming due to the development of pathogenic synergy with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).4–6 Although TB drug development has made substantial progress in the past decade and different drug classes are in development, there is still a need of novel potent chemical entities provided with promising antimycobacterial activities.7Chromene (benzopyran), an important class of benzo-fused oxaheterocycles is an integral part of many bioactive compounds exhibiting a wide range of biological properties including anti-HIV,8–10 anticancer,11,12 antimicrobial,13,14 antitumor,15 antiviral,16 anti-inflammatory17 and antioxidant18 activities. Among naturally occurring chromene heterocycles, molecules like dehydrolupinifolinol (I), eriosemaone A (II), karanjachromene (III), (+)-calanolide A (IV) and benzofuro-chromene (V) were reported as anti-tubercular agents (Fig. 1).19–22 On the other hand, synthesis of triazole-fused compounds approached through click reaction continues to fascinate the attention of chemists, in a bid to identify molecules with enhanced pharmacological properties.23 Moreover, compounds consisting 1,2,3-triazole ring fused with various carbocyclic moieties exhibited remarkable biological activities, e.g., 1,2,3-triazolo[1,5-a]quinoxaline possess good affinity toward benzodiazepine and adenosine receptors24,25 and the morpholine-fused triazole is efficient γ-secretase modulator (GSM) for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.26 Additionally, 1,2,3-triazoles conjugated with different sorts of heterocyclic moieties were reported to exhibit potent anti-tubercular activity (VI–XI) (Fig. 2).27–30
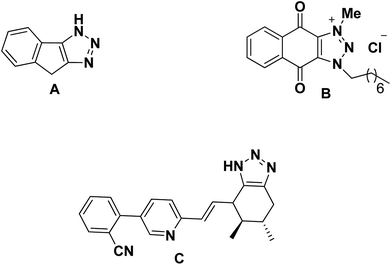
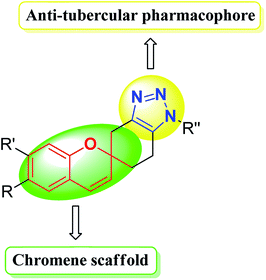
Therefore the triazole-fused structural motifs became increasingly common in pharmaceutical targets and in a wide array of bioactive molecules such as chemotherapeutic A,31 antibacterial B32 and cardiovascular C33 agents (Fig. 3). Inspired by the frequent occurrence of 1,2,3-triazole or chromene framework in various biologically active anti-tubercular agents and in continuation to our ongoing efforts34,35 in exploiting the biological significance of 1,2,3-triazole nuclei fused with various carbocyclic frameworks, we anticipated that integration of these two frameworks in a single molecule may provide truly effective lead structures (Fig. 4) and they are further evaluated against the Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv strain. To the best of our knowledge, synthesis and antimycobacterial activities of these 1,2,3-triazole-fused spirochromene conjugates are unprecedented.
Results and discussion
Chemistry
The strategy adopted for synthesis of 1,2,3-triazole-fused spirochromene scaffolds, is depicted in Scheme 1. In the first step, Kabbe condensation of substituted acetophenones 1a–c with 1,4-dioxaspiro[4.5]decan-8-one 2, in the presence of pyrrolidine gave corresponding dispiro[chromane-2,1′-cyclohexane-4′,2′′-[1,3]dioxolan]-4-ones 3a–c.36,37 Subsequently, these were subjected to reduction using sodium borohydride (NaBH4) to afford the spirochromanols 4a–c.38 The following spirochromanols 4a–c on deprotection and dehydration with excess 6 N HCl provided the corresponding spirochromene 5a–c.39,40 Thus obtained spirochromenes 5a–c on [3 + 2] Huisgen cycloaddition using a catalytic amount of pyrrolidine, with various aryl azides 6a–e,41 furnished 1,2,3-triazole-fused spirochromene scaffolds 7a–o in low to moderate yields (Scheme 1 & Fig. 5).42,43The synthesized 1,2,3-triazole-fused spirochromene scaffolds were characterized by 1H NMR, 13C NMR, mass and FTIR spectral analysis; X-ray diffractometry confirmed the structure of compound 7a (CCDC 1820092†)44 as shown in Fig. 6.
 | ||
| Fig. 6 A view of KA357, showing the atom-labelling scheme of compound 7a. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level and H atoms are represented by circles of arbitrary radii. | ||
Anti-tubercular assay
| Compounds | MIC (μg mL−1) | MIC (μM) | Cytotoxicity in % inhibition at 50 μg mL−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| a * Represent more active compounds; MIC: minimum inhibitory concentration (the lowest concentration that inhibited the bacterial growth). MIC values are interpreted as an average of duplicates. ND = not determined. | |||
| 7a* | 1.56 | 4.74 | 30.23 |
| 7b | >25 | 75.80 | ND |
| 7c | 12.5 | 34.43 | ND |
| 7d* | 1.56 | 4.34 | 33.14 |
| 7e | >25 | 75.80 | ND |
| 7f | 6.25 | 17.90 | 21.41 |
| 7g | 25 | 68.87 | ND |
| 7h | 25 | 65.27 | ND |
| 7i* | 1.56 | 4.11 | 29.36 |
| 7j | 12.5 | 34.43 | ND |
| 7k* | 3.125 | 8.60 | 24.90 |
| 7l | >25 | 68.96 | ND |
| 7m* | 3.125 | 7.87 | 24.76 |
| 7n | 6.25 | 15.90 | 22.64 |
| 7o | 25 | 66.31 | ND |
| Isoniazid | 0.055 | 0.437 | ND |
| Rifampicin | 0.411 | 0.50 | ND |
| Ethambutol | 1.56 | 7.64 | ND |
As observed from Table 1, the tested compounds showed antimycobacterial activity with MIC values between 4.11 and 75.80 μM. Out of the various compounds tested, compounds 7a, 7c, 7d, 7f, 7i, 7j, 7k, 7m and 7n with MIC values varying from 4.11 to 50.40 μM possess more inhibitory efficiency compared to that of standard pyrazinamide (MIC = 50.77 μM). Compounds 7a, 7d and 7i were found to possess excellent potency i.e. 4.74 μM, 4.34 μM and 4.11 μM respectively, while compounds 7k (8.6 μM) and 7m (7.67 μM) were close as compared to first line anti-tubercular drug ethambutol (MIC = 7.64 μM). However, all the compounds exhibited lower inhibitory efficiency compared to isoniazid (MIC = 0.437 μM) and rifampicin (MIC = 0.5 μM).
Experimental
All the reagents and solvents were purchased from commercial sources. Reactions were monitored by thin layer chromatography (TLC) on silica gel plates (60 F254), visualization done by exposing to iodine vapour and ultraviolet light. Column chromatography was performed on silica gel (60–120 mesh) using distilled hexane, acetone. 1H NMR (400 MHz) and 13C NMR (100 MHz) spectra were recorded in CDCl3 or DMSO-d6 solvents by using Bruker Avance II 400 spectrometer. Proton chemical shifts (δ) are relative to tetramethylsilane (TMS, δ = 0.00) as internal standard and expressed in ppm. Spin multiplicities are given as s (singlet), d (doublet), dd (doublet of doublet), td (triplet of doublet) and m (multiplet). Coupling constants (J) are given in hertz. Mass spectra were recorded on GCMS-QP 1000 EX mass spectrometer. Infrared spectra were recorded on a Shimadzu FT-IR-8400s spectrometer. Melting points were determined using melting point apparatus and are uncorrected.General procedure for the synthesis of compound (3a–c)
To a solution of 1,4-dioxaspiro[4.5]decan-8-one (2) (156 mg, 1 mmol) in dry ethanol, a catalytic amount of pyrrolidine was added followed by a substituted 2′-hydroxyacetophenones (1a–c) (1 mmol). The reaction mixture was heated under reflux for 8–10 h with constant stirring. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue was dissolved in ethyl acetate. The mixture was washed with a 1 M aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid, with a 1 M aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide and brine. The organic extracts were dried over sodium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting crude product was purified by column chromatography (eluent: PE/acetone mixtures of increasing polarity) to obtain the compounds 6,7-substituted dispiro[chromane-2,1′-cyclohexane-4′,2′′-[1,3]dioxolan]-4-ones (3a–c) as white solids.General procedure for the synthesis of compound (4a–c)
To a stirred suspension of sodium borohydride (37.83 mg, 1 mmol) in MeOH, a solution of 6,7-substituted dispiro[chromane-2,1′-cyclohexane-4′,2′′-[1,3]dioxolan]-4-ones (3a–c) (1 mmol) in MeOH was added drop wise at 0 °C through an addition funnel. The resulting mixture was allowed to stir at room temperature for 1 h. The reaction mixture was concentrated in vacuo, poured into ice and saturated NaHCO3 aqueous solution and extracted with EtOAc. The combined organics were washed with brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated in vacuo to give 6,7-substituted dispiro[chromane-2,1′-cyclohexane-4′,2′′-[1,3]dioxolan]-4-ols (4a–c) as white solids.General procedure for the synthesis of compound (5a–c)
In a round bottom flask the previous spiro compounds (4a–c) dissolved in acetone was taken. To this solution excess amount of 6 N HCl was added at room temperature. The reaction was allowed to stir at room temperature until the ketal has consumed totally (monitored by TLC). After completion of the reaction, the reaction mixture was slowly quenched with saturated aqueous NaHCO3 until pH 7 was reached. The solution was diluted with ethyl acetate. The phases were separated and the aqueous phase was back-extracted with ethyl acetate twice. The combined organic phases were washed with brine, dried over Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under reduce pressure. The crude material was purified by flash chromatography (PE/acetones as the eluents). The corresponding fractions were combined and concentrated under reduce pressure yielding 6,7-substituted spiro[chromene-2,1′-cyclohexan]-4′-ones (5a–c) as white solids.General procedure for the synthesis of compound (7a–o)
The catalyst pyrrolidine (0.1 mmol) was added to a solution of aryl azides 6a–e (0.5 mmol) and compound 5a–c (1 mmol) in DMSO and the reaction mixture was stirred at 80 °C for 24 h. The completion of the reaction was confirmed by TLC (PE/EtOAc 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2). The crude product was purified by column chromatography on silica gel, eluting with PE/acetone (10
2). The crude product was purified by column chromatography on silica gel, eluting with PE/acetone (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 to 4
1 to 4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), to afford the desired products 7a–o as white solids.
1), to afford the desired products 7a–o as white solids.
Antimycobacterial activity
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20; 100 μL was used as inoculum. Each drug stock solution was thawed and diluted in 7H9-S at four-fold the final highest concentration tested. Serial two-fold dilutions of each drug were prepared directly in a sterile 96-well microtiter plate using 100 μL 7H9-S. A growth control containing no antibiotic and a sterile control were also prepared on each plate. Sterile water was added to all perimetre wells to avoid evaporation during the incubation. The plate was covered, sealed in plastic bags and incubated at 37 °C in normal atmosphere. After 7 days incubation, 30 μL of alamar blue solution was added to each well, and the plate was re-incubated overnight. A change in colour from blue (oxidised state) to pink (reduced) indicated the growth of bacteria, and the MIC was defined as the lowest concentration of drug that prevented this change in colour.45
20; 100 μL was used as inoculum. Each drug stock solution was thawed and diluted in 7H9-S at four-fold the final highest concentration tested. Serial two-fold dilutions of each drug were prepared directly in a sterile 96-well microtiter plate using 100 μL 7H9-S. A growth control containing no antibiotic and a sterile control were also prepared on each plate. Sterile water was added to all perimetre wells to avoid evaporation during the incubation. The plate was covered, sealed in plastic bags and incubated at 37 °C in normal atmosphere. After 7 days incubation, 30 μL of alamar blue solution was added to each well, and the plate was re-incubated overnight. A change in colour from blue (oxidised state) to pink (reduced) indicated the growth of bacteria, and the MIC was defined as the lowest concentration of drug that prevented this change in colour.45*Standards INH & amp; RIF (0.437 & amp; 0.5 μM).
Crystallographic data
X-ray data for the compound 7a (KA357) was collected at room temperature on a Bruker D8 QUEST instrument with an IμS Mo microsource (λ = 0.7107 Å) and a PHOTON-100 detector. The raw data frames were reduced and corrected for absorption effects using the Bruker Apex 3 software suite programs.47 The structure was solved using intrinsic phasing method47 and further refined with the SHELXL48 program and expanded using Fourier techniques. Anisotropic displacement parameters were included for all non-hydrogen atoms. All C bound H atoms were positioned geometrically and treated as riding on their parent C atoms [C–H = 0.93–0.97 Å, and Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq.(C) for methyl H or 1.2Ueq.(C) for other H atoms].![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 247 reflections measured (4.42° ≤ 2Θ ≤ 61.14°), 5166 unique (Rint = 0.0288, Rsigma = 0.0248) which were used in all calculations. The final R1 was 0.0560 (I > 2σ(I)) and wR2 was 0.1638 (all data). CCDC 1820092 contains supplementary crystallographic data for the structure.†
247 reflections measured (4.42° ≤ 2Θ ≤ 61.14°), 5166 unique (Rint = 0.0288, Rsigma = 0.0248) which were used in all calculations. The final R1 was 0.0560 (I > 2σ(I)) and wR2 was 0.1638 (all data). CCDC 1820092 contains supplementary crystallographic data for the structure.†![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). IR (KBr): 2932, 2891, 1689, 1616, 1484 1285, 1136, 1090 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.65 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.32–7.28 (d, J = 8.5, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 6.88 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 4.01–3.92 (m, 4H), 2.69 (s, 2H), 2.30 (s, 3H), 2.15–2.07 (m, 2H), 1.98 (td, J = 13.1, 4.3 Hz, 2H), 1.72 (td, J = 13.1, 4.3 Hz, 2H), 1.63–1.56 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 192.5, 157.3, 137.3, 130.4, 126.2, 120.4, 118.1, 108.0, 78.5, 64.4, 64.3, 48.0, 32.1, 30.0, 20.4. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 289 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C17H20O4: C, 70.81; H, 6.99. Found: C, 70.83; H, 6.97.
1). IR (KBr): 2932, 2891, 1689, 1616, 1484 1285, 1136, 1090 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.65 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.32–7.28 (d, J = 8.5, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 6.88 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 4.01–3.92 (m, 4H), 2.69 (s, 2H), 2.30 (s, 3H), 2.15–2.07 (m, 2H), 1.98 (td, J = 13.1, 4.3 Hz, 2H), 1.72 (td, J = 13.1, 4.3 Hz, 2H), 1.63–1.56 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 192.5, 157.3, 137.3, 130.4, 126.2, 120.4, 118.1, 108.0, 78.5, 64.4, 64.3, 48.0, 32.1, 30.0, 20.4. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 289 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C17H20O4: C, 70.81; H, 6.99. Found: C, 70.83; H, 6.97.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). IR (KBr): 2947, 2884, 1686, 1602, 1467, 1259, 1150, 1091 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.82 (d, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H), 7.42 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.7 Hz, 1H), 6.94 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 4.01–3.92 (m, 4H), 2.71 (s, 2H), 2.15–2.06 (m, 2H), 1.96 (td, J = 13.1, 4.2 Hz, 2H), 1.74 (td, J = 13.1, 4.2 Hz, 2H), 1.63–1.62 (m, 1H), 1.60–1.59 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 191.1, 157.8, 136.1, 126.5, 126.0, 121.5, 120.0, 107.8, 79.2, 64.5, 64.3, 47.6, 32.1, 29.9. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 309 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C16H17ClO4: C, 62.24; H, 5.55. Found: C, 62.28; H, 5.51.
1). IR (KBr): 2947, 2884, 1686, 1602, 1467, 1259, 1150, 1091 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.82 (d, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H), 7.42 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.7 Hz, 1H), 6.94 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 4.01–3.92 (m, 4H), 2.71 (s, 2H), 2.15–2.06 (m, 2H), 1.96 (td, J = 13.1, 4.2 Hz, 2H), 1.74 (td, J = 13.1, 4.2 Hz, 2H), 1.63–1.62 (m, 1H), 1.60–1.59 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 191.1, 157.8, 136.1, 126.5, 126.0, 121.5, 120.0, 107.8, 79.2, 64.5, 64.3, 47.6, 32.1, 29.9. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 309 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C16H17ClO4: C, 62.24; H, 5.55. Found: C, 62.28; H, 5.51.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). IR (KBr): 2926, 2883, 1685, 1606, 1443, 1251, 1168, 1086 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.81 (s, 1H), 6.88 (s, 1H), 4.01–3.91 (m, 4H), 2.68 (s, 2H), 2.37 (s, 3H), 2.10 (dd, J = 15.7, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 1.96 (td, J = 13.1, 4.2 Hz, 2H), 1.73 (td, J = 13.1, 4.2 Hz, 2H), 1.64–1.60 (m, 1H), 1.58–1.55 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 190.9, 157.6, 145.2, 127.2, 126.3, 120.5, 119.8, 107.9, 79.1, 64.5, 64.3, 47.6, 32.1, 29.9, 20.8. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 323 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C17H19ClO4: C, 63.26; H, 5.93. Found: C, 63.28; H, 5.91.
1). IR (KBr): 2926, 2883, 1685, 1606, 1443, 1251, 1168, 1086 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.81 (s, 1H), 6.88 (s, 1H), 4.01–3.91 (m, 4H), 2.68 (s, 2H), 2.37 (s, 3H), 2.10 (dd, J = 15.7, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 1.96 (td, J = 13.1, 4.2 Hz, 2H), 1.73 (td, J = 13.1, 4.2 Hz, 2H), 1.64–1.60 (m, 1H), 1.58–1.55 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 190.9, 157.6, 145.2, 127.2, 126.3, 120.5, 119.8, 107.9, 79.1, 64.5, 64.3, 47.6, 32.1, 29.9, 20.8. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 323 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C17H19ClO4: C, 63.26; H, 5.93. Found: C, 63.28; H, 5.91.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). IR (KBr): 3253, 2930, 2858, 1612, 1441, 1248, 1140, 1090 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 7.20 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 6.91 (dd, J = 8.3, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 6.63 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 5.27 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 1H), 4.67–4.58 (m, 1H), 3.92–3.81 (m, 4H), 2.21 (s, 3H), 2.02 (dd, J = 13.4, 6.3 Hz, 1H), 1.89–1.44 (m, 9H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 150.5, 130.1, 129.8, 128.0, 124.4, 117.2, 108.6, 74.4, 64.3, 64.2, 63.5, 41.9, 34.2, 31.4, 30.0, 20.6. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 313 (100) [M + Na]+. Anal. calcd for C17H22O4: C, 70.32; H, 7.64. Found: C, 70.35; H, 7.61.
1). IR (KBr): 3253, 2930, 2858, 1612, 1441, 1248, 1140, 1090 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 7.20 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 6.91 (dd, J = 8.3, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 6.63 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 5.27 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 1H), 4.67–4.58 (m, 1H), 3.92–3.81 (m, 4H), 2.21 (s, 3H), 2.02 (dd, J = 13.4, 6.3 Hz, 1H), 1.89–1.44 (m, 9H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 150.5, 130.1, 129.8, 128.0, 124.4, 117.2, 108.6, 74.4, 64.3, 64.2, 63.5, 41.9, 34.2, 31.4, 30.0, 20.6. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 313 (100) [M + Na]+. Anal. calcd for C17H22O4: C, 70.32; H, 7.64. Found: C, 70.35; H, 7.61.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). IR (KBr): 3254, 2934, 2886, 1608, 1475, 1241, 1173, 1092 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 7.39 (d, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H), 7.15 (dd, J = 8.7, 2.7 Hz, 1H), 6.79 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 5.50 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, 1H), 4.62–4.70 (m, 1H), 3.92–3.81 (m, 4H), 2.06 (dd, J = 13.5, 6.3 Hz, 1H), 1.89–1.45 (m, 9H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 151.4, 129.3, 127.6, 126.2, 125.3, 118.7, 108.4, 75.2, 64.4, 64.3, 63.1, 41.5, 34.3, 31.3, 30.0. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 333 (100) [M + Na]+. Anal. calcd for C16H19ClO4: C, 61.84; H, 6.16. Found: C, 61.89; H, 6.11.
1). IR (KBr): 3254, 2934, 2886, 1608, 1475, 1241, 1173, 1092 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 7.39 (d, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H), 7.15 (dd, J = 8.7, 2.7 Hz, 1H), 6.79 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 5.50 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, 1H), 4.62–4.70 (m, 1H), 3.92–3.81 (m, 4H), 2.06 (dd, J = 13.5, 6.3 Hz, 1H), 1.89–1.45 (m, 9H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 151.4, 129.3, 127.6, 126.2, 125.3, 118.7, 108.4, 75.2, 64.4, 64.3, 63.1, 41.5, 34.3, 31.3, 30.0. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 333 (100) [M + Na]+. Anal. calcd for C16H19ClO4: C, 61.84; H, 6.16. Found: C, 61.89; H, 6.11.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). IR (KBr): 3254, 2928, 2861, 1616, 1444, 1252, 1168, 1091 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 7.36 (s, 1H), 6.77 (s, 1H), 5.43 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H), 4.67–4.59 (m, 1H), 3.90–3.84 (m, 4H), 2.23 (s, 3H), 2.04 (dd, J = 13.5, 6.2 Hz, 1H), 1.90–1.45 (m, 9H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 151.2, 137.2, 127.9, 125.7, 123.8, 119.4, 108.4, 75.0, 64.4, 64.3, 63.0, 41.7, 34.2, 31.3, 30.0, 19.9. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 347 (100) [M + Na]+. Anal. calcd for C17H21ClO4: C, 62.86; H, 6.52. Found: C, 62.84; H, 6.54.
1). IR (KBr): 3254, 2928, 2861, 1616, 1444, 1252, 1168, 1091 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 7.36 (s, 1H), 6.77 (s, 1H), 5.43 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H), 4.67–4.59 (m, 1H), 3.90–3.84 (m, 4H), 2.23 (s, 3H), 2.04 (dd, J = 13.5, 6.2 Hz, 1H), 1.90–1.45 (m, 9H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 151.2, 137.2, 127.9, 125.7, 123.8, 119.4, 108.4, 75.0, 64.4, 64.3, 63.0, 41.7, 34.2, 31.3, 30.0, 19.9. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 347 (100) [M + Na]+. Anal. calcd for C17H21ClO4: C, 62.86; H, 6.52. Found: C, 62.84; H, 6.54.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). IR (KBr): 3024, 2938, 2868, 1716, 1635, 1485, 1241, 1138 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 6.97 (dd, J = 8.1, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 6.85 (d, J = 1.7 Hz, 1H), 6.78 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.42 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 5.58 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 2.90 (td, J = 14.3, 6.3 Hz, 2H), 2.47–2.36 (m, 2H), 2.32–2.28 (m, 1H), 2.27 (s, 3H), 2.28–2.24 (m, 1H), 1.85 (td, J = 13.8, 5.1 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 210.8, 149.9, 130.8, 129.8, 128.5, 127.1, 124.4, 121.6, 116.1, 74.8, 36.5, 35.3, 20.5. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 229 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C15H16O2: C, 78.92; H, 7.06; found: C, 78.97; H, 7.01.
1). IR (KBr): 3024, 2938, 2868, 1716, 1635, 1485, 1241, 1138 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 6.97 (dd, J = 8.1, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 6.85 (d, J = 1.7 Hz, 1H), 6.78 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.42 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 5.58 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 2.90 (td, J = 14.3, 6.3 Hz, 2H), 2.47–2.36 (m, 2H), 2.32–2.28 (m, 1H), 2.27 (s, 3H), 2.28–2.24 (m, 1H), 1.85 (td, J = 13.8, 5.1 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 210.8, 149.9, 130.8, 129.8, 128.5, 127.1, 124.4, 121.6, 116.1, 74.8, 36.5, 35.3, 20.5. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 229 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C15H16O2: C, 78.92; H, 7.06; found: C, 78.97; H, 7.01.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). IR (KBr): 2944, 2863, 1708, 1630, 1475, 1246, 1199 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.11 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 7.01 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.81 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.39 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.65 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 2.81 (td, J = 14.2, 6.3 Hz, 2H), 2.47–2.36 (m, 2H), 2.34–2.25 (m, 2H), 1.87 (td, J = 13.8, 5.1 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 210.2, 150.6, 129.7, 129.0, 126.3, 123.4, 123.1, 117.7, 75.4, 36.4, 35.3. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 249 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C14H13ClO2: C, 67.61; H, 5.27. Found: C, 67.64; H, 5.24.
1). IR (KBr): 2944, 2863, 1708, 1630, 1475, 1246, 1199 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.11 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 7.01 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.81 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.39 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.65 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 2.81 (td, J = 14.2, 6.3 Hz, 2H), 2.47–2.36 (m, 2H), 2.34–2.25 (m, 2H), 1.87 (td, J = 13.8, 5.1 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 210.2, 150.6, 129.7, 129.0, 126.3, 123.4, 123.1, 117.7, 75.4, 36.4, 35.3. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 249 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C14H13ClO2: C, 67.61; H, 5.27. Found: C, 67.64; H, 5.24.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). IR (KBr): 3021, 2925, 2858, 1720, 1634, 1486, 1226, 1147 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.01 (s, 1H), 6.77 (s, 1H), 6.38 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.59 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 2.81(td, J = 14.2, 6.3 Hz, 2H), 2.44–2.36 (m, 2H), 2.32 (s, 3H), 2.31–2.25 (m, 2H), 1.86 (td, J = 13.8, 5.1 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 210.5, 150.5, 137.1, 128.7, 126.5, 126.4, 123.2, 120.9, 118.7, 75.2, 36.4, 35.3, 20.1. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 262 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C15H15ClO2: C, 68.57; H, 5.75. Found: C, 68.54; H, 5.78.
1). IR (KBr): 3021, 2925, 2858, 1720, 1634, 1486, 1226, 1147 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.01 (s, 1H), 6.77 (s, 1H), 6.38 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.59 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 2.81(td, J = 14.2, 6.3 Hz, 2H), 2.44–2.36 (m, 2H), 2.32 (s, 3H), 2.31–2.25 (m, 2H), 1.86 (td, J = 13.8, 5.1 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 210.5, 150.5, 137.1, 128.7, 126.5, 126.4, 123.2, 120.9, 118.7, 75.2, 36.4, 35.3, 20.1. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 262 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C15H15ClO2: C, 68.57; H, 5.75. Found: C, 68.54; H, 5.78.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2). IR (KBr): 3021, 2925, 2858, 1634, 1486, 1226, 1147 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.65–7.44 (m, 5H), 6.92 (dd, J = 8.1, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 6.86 (d, J = 1.7 Hz, 1H), 6.66 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.47 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 5.69 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 3.42 (d, J = 16.3 Hz, 1H), 3.08–2.92 (m, 2H), 2.81–2.73 (m, 1H), 2.39–2.30 (m, 1H), 2.26 (s, 3H), 1.97–1.86 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 149.9, 141.7, 136.9, 130.9, 130.7, 129.9, 129.5, 128.7, 128.1, 127.1, 124.6, 123.0, 121.2, 116.3, 75.9, 33.6, 32.3, 20.5, 18.0. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 330 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C21H19N3O: C, 76.57; H, 5.81; N, 12.76. Found: C, 76.61; H, 5.82; N, 12.71.
2). IR (KBr): 3021, 2925, 2858, 1634, 1486, 1226, 1147 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.65–7.44 (m, 5H), 6.92 (dd, J = 8.1, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 6.86 (d, J = 1.7 Hz, 1H), 6.66 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.47 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 5.69 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 3.42 (d, J = 16.3 Hz, 1H), 3.08–2.92 (m, 2H), 2.81–2.73 (m, 1H), 2.39–2.30 (m, 1H), 2.26 (s, 3H), 1.97–1.86 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 149.9, 141.7, 136.9, 130.9, 130.7, 129.9, 129.5, 128.7, 128.1, 127.1, 124.6, 123.0, 121.2, 116.3, 75.9, 33.6, 32.3, 20.5, 18.0. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 330 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C21H19N3O: C, 76.57; H, 5.81; N, 12.76. Found: C, 76.61; H, 5.82; N, 12.71.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2). IR (KBr): 3036, 2923, 2855, 1645, 1491, 1225, 1150 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.48 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.33 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 6.91 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.85 (s, 1H), 6.65 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.46 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 5.68 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 3.40 (d, J = 16.5 Hz, 1H), 3.04–2.90 (m, 2H), 2.78–2.68 (m, 1H), 2.44 (s, 3H), 2.37–2.28 (m, 1H), 2.26 (s, 3H), 1.96–1.86 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 149.9, 141.5, 138.8, 134.4, 130.9, 130.6, 130.1, 129.9, 128.1, 127.1, 124.5, 122.9, 121.2, 116.3, 75.9, 33.6, 32.2, 21.2, 20.5, 17.9. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 344.30 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C22H21N3O: C, 76.94; H, 6.16; N, 12.24. Found: C, 76.98; H, 6.15; N, 12.27.
2). IR (KBr): 3036, 2923, 2855, 1645, 1491, 1225, 1150 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.48 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.33 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 6.91 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.85 (s, 1H), 6.65 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.46 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 5.68 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 3.40 (d, J = 16.5 Hz, 1H), 3.04–2.90 (m, 2H), 2.78–2.68 (m, 1H), 2.44 (s, 3H), 2.37–2.28 (m, 1H), 2.26 (s, 3H), 1.96–1.86 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 149.9, 141.5, 138.8, 134.4, 130.9, 130.6, 130.1, 129.9, 128.1, 127.1, 124.5, 122.9, 121.2, 116.3, 75.9, 33.6, 32.2, 21.2, 20.5, 17.9. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 344.30 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C22H21N3O: C, 76.94; H, 6.16; N, 12.24. Found: C, 76.98; H, 6.15; N, 12.27.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2). IR (KBr): 3031, 2938, 2866, 1595, 1496, 1223, 1147 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.62–7.48 (m, 4H), 6.95–6.89 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.85 (s, 1H), 6.64 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.47 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 5.68 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 3.41 (d, J = 16.5 Hz, 1H), 3.08–2.89 (m, 2H), 2.79–2.70 (m, 1H), 2.40–2.31 (m, 1H), 2.44 (s, 3H), 1.96–1.85 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 149.9, 141.9, 135.4, 134.6, 130.9, 130.7, 130.0, 129.8, 128.0, 127.1, 124.6, 124.1, 121.1, 116.3, 75.7, 33.5, 32.2, 20.5, 18.0. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 364 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C21H18ClN3O: C, 69.32; H, 4.99; N, 11.55. Found: C, 69.30; H, 4.97; N, 11.59.
2). IR (KBr): 3031, 2938, 2866, 1595, 1496, 1223, 1147 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.62–7.48 (m, 4H), 6.95–6.89 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.85 (s, 1H), 6.64 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.47 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 5.68 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 3.41 (d, J = 16.5 Hz, 1H), 3.08–2.89 (m, 2H), 2.79–2.70 (m, 1H), 2.40–2.31 (m, 1H), 2.44 (s, 3H), 1.96–1.85 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 149.9, 141.9, 135.4, 134.6, 130.9, 130.7, 130.0, 129.8, 128.0, 127.1, 124.6, 124.1, 121.1, 116.3, 75.7, 33.5, 32.2, 20.5, 18.0. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 364 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C21H18ClN3O: C, 69.32; H, 4.99; N, 11.55. Found: C, 69.30; H, 4.97; N, 11.59.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2). IR (KBr): 3015, 2924, 2854, 1590, 1482, 1252, 1149 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.50 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H), 7.03 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H), 6.91 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.85 (s, 1H), 6.65 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.46 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 5.68 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.40 (d, J = 16.4 Hz, 1H), 3.01–2.91 (m, 2H), 2.75–2.66 (m, 1H), 2.36–2.29 (m, 1H), 2.26 (s, 3H), 1.96–1.85 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 159.8, 149.9, 141.4, 131.0, 130.6, 129.9, 129.9, 128.1, 127.1, 124.6, 124.5, 121.2, 116.3, 114.6, 75.9, 55.6, 33.7, 32.2, 20.5, 17.8. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 360 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C22H21N3O2: C, 73.52; H, 5.89; N, 11.69. Found: C, 73.56; H, 5.90; N, 11.64.
2). IR (KBr): 3015, 2924, 2854, 1590, 1482, 1252, 1149 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.50 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H), 7.03 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H), 6.91 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.85 (s, 1H), 6.65 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.46 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 5.68 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.40 (d, J = 16.4 Hz, 1H), 3.01–2.91 (m, 2H), 2.75–2.66 (m, 1H), 2.36–2.29 (m, 1H), 2.26 (s, 3H), 1.96–1.85 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 159.8, 149.9, 141.4, 131.0, 130.6, 129.9, 129.9, 128.1, 127.1, 124.6, 124.5, 121.2, 116.3, 114.6, 75.9, 55.6, 33.7, 32.2, 20.5, 17.8. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 360 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C22H21N3O2: C, 73.52; H, 5.89; N, 11.69. Found: C, 73.56; H, 5.90; N, 11.64.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2). IR (KBr): 3025, 2937, 2855, 1590, 1488, 1221, 1111 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.40–7.30 (m, 3H), 7.23–7.18 (m, 2H), 6.88 (dd, J = 8.2, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 6.81 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 6.51 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.41 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 5.60 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 5.59 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 2H), 3.31 (d, J = 16.4 Hz, 1H), 2.87 (d, J = 16.4 Hz, 1H), 2.67–2.54 (m, 1H), 2.49–2.39 (m, 1H), 2.24 (s, 3H), 2.20 (m, 1H), 1.89–1.78 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 149.8, 141.5, 134.8, 131.0, 130.6, 129.8, 130.0, 128.4, 128.0, 127.4, 127.0, 124.4, 121.2, 116.2, 75.9, 52.0, 33.6, 31.8, 20.5, 16.5. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 344 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C22H21N3O: C, 76.94; H, 6.16; N, 12.24. Found: C, 76.89; H, 6.18; N, 12.27.
2). IR (KBr): 3025, 2937, 2855, 1590, 1488, 1221, 1111 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.40–7.30 (m, 3H), 7.23–7.18 (m, 2H), 6.88 (dd, J = 8.2, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 6.81 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 6.51 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.41 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 5.60 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 5.59 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 2H), 3.31 (d, J = 16.4 Hz, 1H), 2.87 (d, J = 16.4 Hz, 1H), 2.67–2.54 (m, 1H), 2.49–2.39 (m, 1H), 2.24 (s, 3H), 2.20 (m, 1H), 1.89–1.78 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 149.8, 141.5, 134.8, 131.0, 130.6, 129.8, 130.0, 128.4, 128.0, 127.4, 127.0, 124.4, 121.2, 116.2, 75.9, 52.0, 33.6, 31.8, 20.5, 16.5. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 344 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C22H21N3O: C, 76.94; H, 6.16; N, 12.24. Found: C, 76.89; H, 6.18; N, 12.27.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2). IR (KBr): 3026, 2929, 2845, 1588, 1463, 1206, 1109 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.64–7.45 (m, 5H), 7.07 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 7.02 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.45 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.76 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 3.41 (d, J = 16.7 Hz, 1H), 3.09–2.94 (m, 2H), 2.84–2.75 (m, 1H), 2.39–2.31 (m, 1H), 1.99–1.89 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 150.6, 141.3, 136.8, 130.8, 129.6, 129.3, 129.1, 128.8, 126.2, 126.2, 123.5, 123.0, 122.7, 117.8, 76.4, 33.6, 32.4, 18.0. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 350 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C20H16ClN3O: C, 68.67; H, 4.61; N, 12.01. Found: C, 68.65; H, 4.60; N, 12.04.
2). IR (KBr): 3026, 2929, 2845, 1588, 1463, 1206, 1109 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.64–7.45 (m, 5H), 7.07 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 7.02 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.45 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.76 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 3.41 (d, J = 16.7 Hz, 1H), 3.09–2.94 (m, 2H), 2.84–2.75 (m, 1H), 2.39–2.31 (m, 1H), 1.99–1.89 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 150.6, 141.3, 136.8, 130.8, 129.6, 129.3, 129.1, 128.8, 126.2, 126.2, 123.5, 123.0, 122.7, 117.8, 76.4, 33.6, 32.4, 18.0. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 350 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C20H16ClN3O: C, 68.67; H, 4.61; N, 12.01. Found: C, 68.65; H, 4.60; N, 12.04.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2). IR (KBr): 3033, 2931, 2847, 1591, 1477, 1209, 1117 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.50–7.45 (m, 2H), 7.36, 7.31 (m, 2H), 7.06 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 7.02 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.44 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.75 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 3.40 (d, J = 17.0 Hz, 1H), 3.05–2.93 (m, 2H), 2.80–2.72 (m, 1H), 2.44 (s, 3H), 2.37–2.30 (m, 1H), 1.93 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 150.7, 141.1, 139.0, 134.4, 130.7, 130.1, 129.3, 129.1, 126.2, 123.5, 122.9, 122.7, 117.8, 76.5, 33.6, 32.4, 21.2, 17.9. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 364 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C21H18ClN3O: C, 69.32; H, 4.99; Cl, 9.74; N, 11.55. Found: C, 69.30; H, 4.97; Cl, 9.74; N, 11.59.
2). IR (KBr): 3033, 2931, 2847, 1591, 1477, 1209, 1117 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.50–7.45 (m, 2H), 7.36, 7.31 (m, 2H), 7.06 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 7.02 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.44 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.75 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 3.40 (d, J = 17.0 Hz, 1H), 3.05–2.93 (m, 2H), 2.80–2.72 (m, 1H), 2.44 (s, 3H), 2.37–2.30 (m, 1H), 1.93 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 150.7, 141.1, 139.0, 134.4, 130.7, 130.1, 129.3, 129.1, 126.2, 123.5, 122.9, 122.7, 117.8, 76.5, 33.6, 32.4, 21.2, 17.9. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 364 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C21H18ClN3O: C, 69.32; H, 4.99; Cl, 9.74; N, 11.55. Found: C, 69.30; H, 4.97; Cl, 9.74; N, 11.59.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2). IR (KBr): 3016, 2955, 2847, 1589, 1486, 1219, 1102 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.60–7.49 (m, 4H), 7.06 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 7.02 (d, J = 2.6 Hz, 1H), 6.68 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.45 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.75 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 3.41 (d, J = 16.6 Hz, 1H), 3.07–2.90 (m, 2H), 2.82–2.73 (m, 1H), 2.40–2.31 (m, 1H), 1.98–1.88 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 150.6, 141.6, 135.3, 134.7, 130.8, 129.8, 129.1, 126.3, 124.1, 123.6, 122.6, 117.8, 76.3, 33.5, 32.3, 18.0. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 384 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C20H15Cl2N3O: C, 62.51; H, 3.93; N, 10.94. Found: C, 62.55; H, 3.92; N, 10.91.
2). IR (KBr): 3016, 2955, 2847, 1589, 1486, 1219, 1102 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.60–7.49 (m, 4H), 7.06 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 7.02 (d, J = 2.6 Hz, 1H), 6.68 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.45 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.75 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 3.41 (d, J = 16.6 Hz, 1H), 3.07–2.90 (m, 2H), 2.82–2.73 (m, 1H), 2.40–2.31 (m, 1H), 1.98–1.88 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 150.6, 141.6, 135.3, 134.7, 130.8, 129.8, 129.1, 126.3, 124.1, 123.6, 122.6, 117.8, 76.3, 33.5, 32.3, 18.0. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 384 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C20H15Cl2N3O: C, 62.51; H, 3.93; N, 10.94. Found: C, 62.55; H, 3.92; N, 10.91.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2). IR (KBr): 3012, 2942, 2841, 1604, 1476, 1219, 1114 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.54–7.46 (m, 2H), 7.09–7.00 (m, 4H), 6.68 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.44 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.76 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.40 (d, J = 16.1 Hz, 1H), 3.02–2.90 (m, 2H), 2.79–2.68 (m, 1H), 2.37–2.29 (m, 1H), 1.98–1.88 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 159.9, 150.7, 141.0, 130.9, 129.3, 129.1, 126.2, 124.6, 123.5, 117.8, 114.7, 76.5, 55.6, 33.6, 32.4, 17.7. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 380 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C21H18ClN3O2: C, 66.40; H, 4.78; N, 11.06. Found: C, 66.45; H, 4.77; N, 11.10.
2). IR (KBr): 3012, 2942, 2841, 1604, 1476, 1219, 1114 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.54–7.46 (m, 2H), 7.09–7.00 (m, 4H), 6.68 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.44 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.76 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.40 (d, J = 16.1 Hz, 1H), 3.02–2.90 (m, 2H), 2.79–2.68 (m, 1H), 2.37–2.29 (m, 1H), 1.98–1.88 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 159.9, 150.7, 141.0, 130.9, 129.3, 129.1, 126.2, 124.6, 123.5, 117.8, 114.7, 76.5, 55.6, 33.6, 32.4, 17.7. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 380 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C21H18ClN3O2: C, 66.40; H, 4.78; N, 11.06. Found: C, 66.45; H, 4.77; N, 11.10.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2). IR (KBr): 3040, 2941, 2865, 1588, 1482, 1208, 1112 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.40–7.31 (m, 3H), 7.23–7.17 (m, 2H), 7.04–7.00 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.99–6.97 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.54 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.39 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.67 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.49 (d, J = 3.1 Hz, 2H), 3.29 (d, J = 16.5 Hz, 1H), 2.88 (d, J = 16.5 Hz, 1H), 2.66–2.54 (m, 1H), 2.52–2.42 (m, 1H), 2.26–2.17 (m, 1H), 1.90–1.81 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 150.6, 141.2, 134.7, 130.9, 129.2, 129.0, 128.4, 127.4, 126.1, 126.1, 123.4, 122.7, 117.7, 76.5, 52.1, 33.5, 31.9, 16.5. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 364 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C21H18ClN3O: C, 69.32; H, 4.99; N, 11.55; O, 4.40. Found: C, 69.38; H, 4.97; N, 11.59.
2). IR (KBr): 3040, 2941, 2865, 1588, 1482, 1208, 1112 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.40–7.31 (m, 3H), 7.23–7.17 (m, 2H), 7.04–7.00 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.99–6.97 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.54 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.39 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.67 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.49 (d, J = 3.1 Hz, 2H), 3.29 (d, J = 16.5 Hz, 1H), 2.88 (d, J = 16.5 Hz, 1H), 2.66–2.54 (m, 1H), 2.52–2.42 (m, 1H), 2.26–2.17 (m, 1H), 1.90–1.81 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 150.6, 141.2, 134.7, 130.9, 129.2, 129.0, 128.4, 127.4, 126.1, 126.1, 123.4, 122.7, 117.7, 76.5, 52.1, 33.5, 31.9, 16.5. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 364 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C21H18ClN3O: C, 69.32; H, 4.99; N, 11.55; O, 4.40. Found: C, 69.38; H, 4.97; N, 11.59.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2). IR (KBr): 3076, 2921, 2849, 1600, 1494, 1251, 1158 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.64–7.45 (m, 5H), 7.01 (s, 1H), 6.65 (s, 1H), 6.43 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.70 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 3.40 (d, J = 16.5 Hz, 1H), 3.08–2.91 (m, 2H), 2.83–2.75 (m, 1H), 2.39–2.30 (m, 1H), 2.28 (s, 3H), 1.97–1.87 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 150.5, 141.4, 137.2, 136.8, 130.8, 129.6, 128.8, 128.3, 126.5, 126.3, 123.4, 123.0, 120.5, 118.9, 76.3, 33.5, 32.3, 20.1, 18.0. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 364 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C21H18ClN3O: C, 69.32; H, 4.99; N, 11.55. Found: C, 69.35; H, 4.98; N, 11.57.
2). IR (KBr): 3076, 2921, 2849, 1600, 1494, 1251, 1158 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.64–7.45 (m, 5H), 7.01 (s, 1H), 6.65 (s, 1H), 6.43 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.70 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 3.40 (d, J = 16.5 Hz, 1H), 3.08–2.91 (m, 2H), 2.83–2.75 (m, 1H), 2.39–2.30 (m, 1H), 2.28 (s, 3H), 1.97–1.87 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 150.5, 141.4, 137.2, 136.8, 130.8, 129.6, 128.8, 128.3, 126.5, 126.3, 123.4, 123.0, 120.5, 118.9, 76.3, 33.5, 32.3, 20.1, 18.0. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 364 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C21H18ClN3O: C, 69.32; H, 4.99; N, 11.55. Found: C, 69.35; H, 4.98; N, 11.57.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2). IR (KBr): 3081, 2926, 2864, 1605, 1488, 1256, 1158 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.51–7.46 (m, 2H), 7.31–7.36 (m, 2H), 7.01 (s, 1H), 6.65 (s, 1H), 6.42 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.69 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 3.39 (d, J = 16.6 Hz, 1H), 3.04–2.91 (m, 2H), 2.80–2.72 (m, 1H), 2.44 (s, 3H), 2.37–2.29 (m, 1H), 2.28 (s, 3H), 1.97–1.87 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 150.5, 141.3, 138.9, 137.1, 134.4, 130.8, 130.1, 128.3, 126.4, 126.3, 123.4, 122.9, 120.5, 118.9, 76.3, 33.6, 32.3, 21.2, 20.1, 17.9. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 378 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C22H20ClN3O: C, 69.93; H, 5.33; N, 11.12. Found: C, 69.97; H, 5.35; N, 11.06.
2). IR (KBr): 3081, 2926, 2864, 1605, 1488, 1256, 1158 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.51–7.46 (m, 2H), 7.31–7.36 (m, 2H), 7.01 (s, 1H), 6.65 (s, 1H), 6.42 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.69 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 3.39 (d, J = 16.6 Hz, 1H), 3.04–2.91 (m, 2H), 2.80–2.72 (m, 1H), 2.44 (s, 3H), 2.37–2.29 (m, 1H), 2.28 (s, 3H), 1.97–1.87 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 150.5, 141.3, 138.9, 137.1, 134.4, 130.8, 130.1, 128.3, 126.4, 126.3, 123.4, 122.9, 120.5, 118.9, 76.3, 33.6, 32.3, 21.2, 20.1, 17.9. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 378 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C22H20ClN3O: C, 69.93; H, 5.33; N, 11.12. Found: C, 69.97; H, 5.35; N, 11.06.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2). IR (KBr): 3089, 2922, 2848, 1606, 1494, 1257, 1156 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.60–7.49 (m, 4H), 7.01 (s, 1H), 6.64 (s, 1H), 6.44 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.69 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 3.40 (d, J = 16.6 Hz, 1H), 3.07–2.89 (m, 2H), 2.82–2.73 (m, 1H), 2.39–2.32 (m, 1H), 2.28 (s, 3H), 1.96–1.87 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 150.4, 141.7, 137.2, 135.3, 134.7, 130.8, 129.8, 128.2, 126.5, 126.3, 124.1, 123.5, 120.5, 118.8, 76.1, 33.4, 32.3, 20.1, 18.0. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 398 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C21H17Cl2N3O: C, 63.33; H, 4.30; N, 10.55. Found: C, 63.31; H, 4.29; N, 10.58.
2). IR (KBr): 3089, 2922, 2848, 1606, 1494, 1257, 1156 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.60–7.49 (m, 4H), 7.01 (s, 1H), 6.64 (s, 1H), 6.44 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.69 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 3.40 (d, J = 16.6 Hz, 1H), 3.07–2.89 (m, 2H), 2.82–2.73 (m, 1H), 2.39–2.32 (m, 1H), 2.28 (s, 3H), 1.96–1.87 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 150.4, 141.7, 137.2, 135.3, 134.7, 130.8, 129.8, 128.2, 126.5, 126.3, 124.1, 123.5, 120.5, 118.8, 76.1, 33.4, 32.3, 20.1, 18.0. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 398 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C21H17Cl2N3O: C, 63.33; H, 4.30; N, 10.55. Found: C, 63.31; H, 4.29; N, 10.58.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2). IR (KBr): 3058, 2926, 2844, 1609, 1445, 1256, 1159 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.55–7.47 (m, 2H), 7.07–6.99 (m, 3H), 6.64 (s, 1H), 6.43 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.70 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.39 (d, J = 16.6 Hz, 1H), 3.01–2.90 (m, 2H), 2.78–2.68 (m, 1H), 2.37–2.28 (m, 1H), 2.28 (s, 3H), 1.96–1.87 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 159.8, 150.5, 141.1, 137.1, 130.9, 129.9, 128.3, 126.4, 126.3, 124.6, 123.4, 120.5, 118.9, 114.7, 76.3, 55.6, 33.6, 32.3, 20.1, 17.7. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 394 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C22H20ClN3O2: C, 67.09; H, 5.12; N, 10.67. Found: C, 67.12; H, 5.13; N, 10.71.
2). IR (KBr): 3058, 2926, 2844, 1609, 1445, 1256, 1159 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.55–7.47 (m, 2H), 7.07–6.99 (m, 3H), 6.64 (s, 1H), 6.43 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.70 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.39 (d, J = 16.6 Hz, 1H), 3.01–2.90 (m, 2H), 2.78–2.68 (m, 1H), 2.37–2.28 (m, 1H), 2.28 (s, 3H), 1.96–1.87 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 159.8, 150.5, 141.1, 137.1, 130.9, 129.9, 128.3, 126.4, 126.3, 124.6, 123.4, 120.5, 118.9, 114.7, 76.3, 55.6, 33.6, 32.3, 20.1, 17.7. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 394 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C22H20ClN3O2: C, 67.09; H, 5.12; N, 10.67. Found: C, 67.12; H, 5.13; N, 10.71.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2). IR (KBr): 3053, 2924, 2851, 1602, 1490, 1252, 1156 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.41–7.32 (m, 3H), 7.23–7.18 (m, 2H), 6.97 (s, 1H), 6.49 (s, 1H), 6.37 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.61 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.49 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H), 3.29 (d, J = 16.4 Hz, 1H), 2.86 (d, J = 16.4 Hz, 1H), 2.67–2.56 (m, 1H), 2.50–2.41 (m, 1H), 2.24 (s, 3H), 2.17–2.34 (m, 1H), 1.89–1.79 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 150.4, 141.3, 137.0, 134.8, 130.9, 129.0, 128.4, 128.2, 127.5, 126.4, 126.2, 123.3, 120.5, 118.8, 76.3, 52.1, 33.5, 31.9, 20.1, 16.5. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 378 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C22H20ClN3O: C, 69.93; H, 5.33; N, 11.12. Found: C, 69.99; H, 5.30; N, 11.09.
2). IR (KBr): 3053, 2924, 2851, 1602, 1490, 1252, 1156 cm−1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.41–7.32 (m, 3H), 7.23–7.18 (m, 2H), 6.97 (s, 1H), 6.49 (s, 1H), 6.37 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.61 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.49 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H), 3.29 (d, J = 16.4 Hz, 1H), 2.86 (d, J = 16.4 Hz, 1H), 2.67–2.56 (m, 1H), 2.50–2.41 (m, 1H), 2.24 (s, 3H), 2.17–2.34 (m, 1H), 1.89–1.79 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 150.4, 141.3, 137.0, 134.8, 130.9, 129.0, 128.4, 128.2, 127.5, 126.4, 126.2, 123.3, 120.5, 118.8, 76.3, 52.1, 33.5, 31.9, 20.1, 16.5. MS (ESI) m/z (%) = 378 (100) [M + H]+. Anal. calcd for C22H20ClN3O: C, 69.93; H, 5.33; N, 11.12. Found: C, 69.99; H, 5.30; N, 11.09.Conclusion
In conclusion, a series of 1,2,3-triazole-fused spirochromene motifs were synthesized for the first time in four steps via [3 + 2] Huisgen cycloaddition starting from 2-hydroxy acetophenone and all these new compounds were confirmed by 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR and MS spectra. The single X-ray diffraction study was used to confirm the molecular structure of a representative compound 7a unambiguously. The in vitro antimycobacterial evaluation showed that most of the synthesized 1,2,3-triazole-fused spirochromenes exhibited moderate to good antimycobacterial activity. Noticeably, compounds 7a, 7d and 7i most potent compound in vitro with MIC of 1.56 μg, against MTB. These findings demonstrated that 1,2,3-triazole-fused spirochromenes have biological significance; further optimization of these identified hits as well as structural modifications are in progress in order to enhance the efficacy against M. tuberculosis.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
The authors thank The Head, Department of Chemistry, Osmania University, Hyderabad, for providing laboratory facilities. P. Chiranjeevi grateful to UGC, New Delhi for PhD fellowship. We thank CFRD analytical team for providing spectral analysis facilities.Notes and references
- World Health Organization, Global tuberculosis report, 2017, only available online: http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en Search PubMed.
- World Health Organization, Global tuberculosis report, 2013, only available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/91355/1/9789241564656_eng.pdf Search PubMed.
- A. Pawlowski, M. Jansson, M. Sköld, M. E. Rottenberg and G. Källenius, PLoS Pathog., 2012, 8, e1002464 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Loddenkemper, D. Sagebiel and A. Brendel, Eur. Respir. J., 2002,(suppl. 36), 66s CrossRef CAS.
- N. Boechat, V. F. Ferreira, S. B. Ferreira, M. d. L. G. Ferreira, F. d. C. da Silva, M. M. Bastos, M. d. S. Costa, M. C. S. Lourenço, A. C. Pinto, A. U. Krettli, A. C. Aguiar, B. M. Teixeira, N. V. da Silva, P. R. C. Martins, F. A. F. M. Bezerra, A. L. S. Camilo, G. P. da Silva and C. C. P. Costa, J. Med. Chem., 2011, 54, 5988 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Cappoen, P. Claes, J. Jacobs, R. Anthonissen, V. Mathys, L. Verschaeve, K. Huygen and N. D. Kimpe, J. Med. Chem., 2014, 57, 2895 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhang, K. Post-Martens and S. Denkin, Drug Discovery Today, 2006, 11, 21 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Kashman, K. R. Gustafson, R. W. Fuller, J. H. Cardellina 2nd, J. B. McMahon, M. J. Currens, R. W. Buckheit Jr, S. H. Hughes, G. M. Cragg and M. R. Boyd, J. Med. Chem., 1992, 35, 2735 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. T. Flavin, J. D. Rizzo, A. Khilevich, A. Kucherenko, A. K. Sheinkman, V. Vilaychack, L. Lin, W. Chen, E. M. Greenwood, T. Pengsuparp, J. M. Pezzuto, S. H. Hughes, T. M. Flavin, M. Cibulski, W. A. Boulanger, R. L. Shone and Z. Q. Xu, J. Med. Chem., 1996, 39, 1303 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Kashiwada, K. Yamazaki, Y. Ikeshiro, T. Yamagishi, T. Fujioka, K. Mihashi, K. Mizuki, L. M. Cosentino, K. Fowke, S. L. Morris-Natschke and K.-H. Lee, Tetrahedron, 2001, 57, 1559 CrossRef CAS.
- J. L. Lopez-Perez, D. A. Olmedo, E. Del Olmo, Y. Vasquez, P. N. Solis, M. P. Gupta and A. San Feliciano, J. Nat. Prod., 2005, 68, 369 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. J. Chang, H. An, K. S. Kim, H. H. Kim, J. Jung, J. M. Lee, N. J. Kim, Y. T. Han, H. Yun, S. Lee, G. Lee, S. Lee, J. S. Lee, J. H. Cha, J. H. Park, J. W. Park, S. C. Lee, S. G. Kim, J. H. Kim, H. Y. Lee, K. W. Kim and Y. G. Suh, J. Med. Chem., 2012, 55, 10863 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. W. Brown, S. Liu, J. Klucik, K. D. Berlin, P. J. Brennan, D. Kaur and D. M. Benbrook, J. Med. Chem., 2004, 47, 1008 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Thareja, A. Verma, A. Kalra, S. Gosain, P. V. Rewatkar and G. R. Kokil, Acta Pol. Pharm., 2010, 67, 423 CAS.
- S. J. Mohr, M. A. Chirigos, F. S. Fuhrman and J. W. Pryor, Cancer Res., 1975, 35, 3750 CAS.
- Q.-F. Hu, B. Zhou, J.-M. Huang, X.-M. Gao, L.-D. Shu, G.-Y. Yang and C.-T. Che, J. Nat. Prod., 2013, 76, 292 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S.-Y. Cheng, K.-J. Huang, S.-K. Wang, Z.-H. Wen, P.-W. Chen and C.-Y. Duh, J. Nat. Prod., 2010, 73, 771 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Gregor, G. Grabner, C. Adelwöhrer, T. Rosenau and L. Gille, J. Org. Chem., 2005, 70, 3472 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Sutthivaiyakit, O. Thongnak, T. Lhinhatrakool, O. Yodchun, R. Srimark, P. Dowtaisong and M. Chuankamnerdkarn, J. Nat. Prod., 2009, 72, 1092 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P.-C. Pan, M.-J. Cheng, C.-F. Peng, H.-Y. Huang, J.-J. Chen and I.-S. Chen, J. Nat. Prod., 2010, 73, 890 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Q. Xu, W. W. Barrow, W. J. Suling, L. Westbrook, E. Barrow, Y. M. Lin and M. T. Flavin, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2004, 12, 1199 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Termentzi, I. Khouri, T. Gaslonde, S. Prado, B. Saint-Joanis, F. Bardou, E. P. Amanatiadou, I. S. Vizirianakis, J. Kordulakova, M. Jackson, R. Brosch, Y. L. Janin, M. Daffé, F. Tillequin and S. Michel, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2010, 45, 5833 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Siddiqui, W. Ahsan, M. S. Alam, R. Alia, S. Jain, B. Azad and J. Akhtar, Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 2011, 8, 161 CAS.
- G. Biagi, I. Giorgi, O. Livi, V. Scartoni, L. Betti, G. Giannaccini and M. L. Trincavelli, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2002, 37, 565 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Bertelli, G. Biagi, I. Giorgi, C. Manera, O. Livi, V. Scartoni, L. Betti, G. Giannaccini, L. Trincavelli and P. L. Barili, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 1998, 33, 113 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Whittaker, C. Steele, D. Hardick, M. Dale, V. Pomel, A. Quattropani, D. Beher, Eur. Pat. Appl., EP 2 687 528 A1, 2014.
- C. Menendez, S. Gau, C. Lherbet, F. Rodriguez, C. Inard, M. R. Pasca and M. Baltas, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2011, 46, 5524 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Gill, G. Jadhav, M. Shaikh, R. Kale, A. Ghawalkar, D. Nagargoje and M. Shiradkar, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2008, 18, 6244 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Kim, S.-N. Cho, T. Oh and P. Kim, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2012, 22, 6844 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Zhou, Y. He, X. Zhang, J. Xu, Y. Luo, Y. Wang, S. G. Franzblau, Z. Yang, R. J. Chan, Y. Liu, J. Zheng and Z.-Y. Zhang, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2010, 107, 4573 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. S. Kallander, Q. Lu, W. Chen, T. Tomaszek, G. Yang, D. Tew, T. D. Meek, G. A. Hofmann, C. K. Schulz-Pritchard, W. W. Smith, C. A. Janson, M. D. Ryan, G.-F. Zhang, K. O. Johanson, R. B. Kirkpatrick, T. F. Ho, P. W. Fisher, M. R. Mattern, R. K. Johnson, M. J. Hansbury, J. D. Winkler, K. W. Ward, D. F. Veber and S. K. Thompson, J. Med. Chem., 2005, 48, 5644 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zhang, N. Redman, A. P. Litke, J. Zeng, J. Zhan, K. Y. Chan and C. W. T. Chang, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2011, 19, 498 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Chackalamannil, M. V. Chelliah, Y. Wang and Y. Xia, WO 2 008 042 422 2008.
- A. Dongamanti, V. K. Aamate, M. G. Devulapally, S. Gundu, M. K. Kotni, V. Manga, S. Balasubramanian and P. Ernala, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2015, 25, 898 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Dongamanti, V. K. Aamate, M. G. Devulapally, S. Gundu, S. Balabadra, V. Manga, P. Yogeeswari, D. Sriram and S., Mol. Diversity, 2017, 21, 999 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H.-J. Kabbe and A. Widdig, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl., 1982, 21, 247 CrossRef.
- H. J. Kabbe, Synthesis, 1978, 1978, 886 CrossRef.
- Xu, Zusheng From Faming Zhuanli Shenqing, 103304571, 18 Sep 2013.
- L. W. Dillard, J. Yuan, L. Jia and Y. Zheng, PCT Int, Appl, WO 2010021680, 2010.
- R. A. Glennon and S. M. Liebowitz, J. Med. Chem., 1982, 25, 393 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Zhou, H. Liao, M. Liu, G. Feng, B. Fu, R. Li, M. Cheng, Y. Zhao and P. Gong, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2014, 22, 6438 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Wang, S. Peng, L. J. T. Danence, Y. Gao and J. Wang, Chem.–Eur. J., 2012, 18, 6088 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. J. T. Danence, Y. Gao, M. Li, Y. Huang and J. Wang, Chem.–Eur. J., 2011, 17, 3584 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- CCDC 1820092 contains supplementary crystallographic data for the compound 7a.†.
- L. Collins and S. G. Franzblau, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 1997, 41, 1004 CAS.
- J. van Meerloo, G. J. Kaspers and J. Cloos, Methods Mol. Biol., 2011, 731, 237 CAS.
- Bruker, APEX3, SAINT and SADABS, Bruker AXS, Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2016 Search PubMed.
- G. M. Sheldrick, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. B: Struct. Sci., Cryst. Eng. Mater., 2015, C71, 3–8 CrossRef PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. CCDC 1820092. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/c8ra03197e |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 |