New 3,5-dimethylorsellinic acid-based meroterpenoids with BACE1 and AchE inhibitory activities from Aspergillus terreus†
Abstract
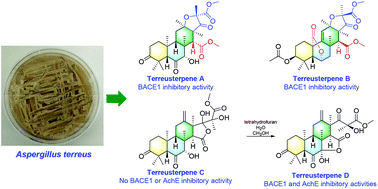
Chemical investigation of the extracts of Aspergillus terreus resulted in the identification of terreusterpenes A–D (1–4), four new 3,5-dimethylorsellinic acid-based meroterpenoids. The structures and absolute configurations of 1–4 were elucidated by spectroscopic analyses including HRESIMS and 1D- and 2D-NMR, chemical conversion, and single crystal X-ray diffraction. Terreusterpenes A (1) and B (2) featured 2,3,5-trimethyl-4-oxo-5-carboxy tetrahydrofuran moieties. Terreusterpene D (4) was characterized by a 4-hydroxy-3-methyl gamma lactone fragment that was generated by accident from the rearrangement of 3 in a mixed tetrahydrofuran–H2O–MeOH solvent. All these compounds were evaluated for the β-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1) and acetylcholinesterase (AchE) inhibitory activities. Among them, compounds 1 and 2 showed potentially significant BACE1 inhibitory activity, with IC50 values of 5.98 and 11.42 μM, respectively. Interestingly, compound 4 exhibited promising BACE1 and AchE inhibitory activities, with IC50 values of 1.91 and 8.86 μM, respectively, while 3 showed no such activity. Taken together, terreusterpenes A and B could be of great importance for the development of new BACE1 inhibitors, while terreusterpene D could serve as the first dual-targeted 3,5-dimethylorsellinic acid-based meroterpenoid for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Biology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...