A novel peptide dendrimer LTP efficiently facilitates transfection of mammalian cells†
Abstract
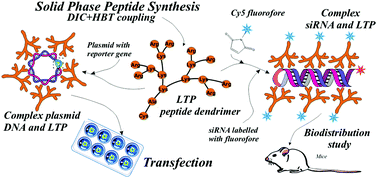
One of the urgent problems of gene therapy is the search for effective transfection methods. Synthetic cationic peptides (CPs) are considered to be one of the most promising approaches for intracellular transport of oligonucleotides. Almost unlimited possibilities of the architectural design of CPs (linear and cyclic structures with a variation of chirality as well as dendrimers) make CPs an effective tunable carrier in this field. Cationic peptide dendrimers (PDs), as a relatively new direction, have significant advantages as gene delivery vehicles by virtue of non-natural ε-amide bonds that significantly increase their resistance to proteolysis. Moreover they also possess much lower cytotoxicity than linear peptides, which is crucial for the potential clinical application of CPs. In a further development of oligonucleotide delivery systems, we have synthesized a collection of 14 CPs, including linear peptides, lipopeptides and PDs. Their activity was evaluated by transfection of 293T cells with plasmids containing reporter genes encoding luciferase or a green fluorescent protein. The obtained results demonstrated that the greatest activity was exhibited by PDs, particularly LTP, an arginine-rich peptide dendrimer, which possesses low cytotoxic and hemolytic activity. The peptide exhibited high cell-penetrating activity, confirmed by fast dissipation of the membrane potential of cells probed by dis-C3-(5). The quantitative analysis of labelled LTP in tissue samples of mice revealed that the Cy5–LTP/siRNA complexes have a reasonable tropism to lung tissues.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Biology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...