Grain engineering by ultrasonic substrate vibration post-treatment of wet perovskite films for annealing-free, high performance, and stable perovskite solar cells†
Abstract
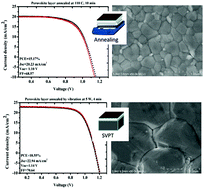
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have gained great interest, owing to a fast increase in their power conversion efficiency (PCE), within a few years. However, their wide application and scale-up are hampered due to multiple obstacles, such as chemical instability, which leads to a short lifetime, and their complicated reaction and crystallization, which requires thermal annealing. Here, we address these issues using the ultrasonic substrate vibration post treatment (SVPT) applied on the as-spun perovskite wet films, so as to achieve a uniform, microscale and stable mixed-halide and mixed-cation perovskite layer, (FAPbI3)0.85(MAPbBr3)0.15, without the need for a conventional thermal annealing step. This is achieved by the creation of fluid micromixing and in situ annealing within the solution, caused by the ultrasonic excitation of the wet film. The optoelectronic properties of the perovskite films subjected to the SVPT, including photoemission, carrier lifetime and band gap, are remarkably improved compared to the conventionally annealed films. When incorporated into a planar PSC, a maximum PCE of 18.55% was achieved, compared to 15.17% for the control device, with high reproducibility and no hysteresis, and the device retained 80% of its initial PCE, over a period of 20 days of storage under ambient conditions.
- This article is part of the themed collection: International Year of the Periodic Table : From Pb and Sn Perovskites to the Next Generation


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...