One-step synthesis of hollow C-NiCo2S4 nanostructures for high-performance supercapacitor electrodes†
Abstract
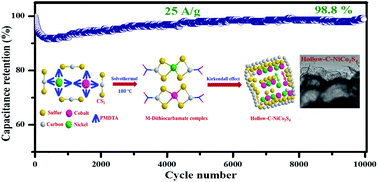
Carbon-containing NiCo2S4 hollow-nanoflake structures were fabricated by a one-step solvothermal method using CS2 as a single source for sulfidation and carbonization. The reaction mechanism for the hollow structure with carbon residues was explored based on the formation of a bis(dithiocarbamate)–metal complex and the Kirkendall effect during solvothermal synthesis. The NiCo2S4 nanoflake electrode exhibited a high specific capacitance of 1722 F g−1 (specific capacity 688.8 C g−1) at a current density of 1 A g−1 and an excellent cycling stability (capacity retention of 98.8% after 10 000 cycles). The as-fabricated asymmetric supercapacitor based on NiCo2S4 nanoflakes and activated carbon electrodes revealed a high energy density of 38.3 W h kg−1 and a high power density of 8.0 kW kg−1 with a capacitance retention of 91.5% and a coulombic efficiency of 95.6% after 5000 cycles, highlighting its great potential for practical supercapacitor applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...