Electrically conductive nanocomposite hydrogels embedded with functionalized carbon nanotubes for spinal cord injury†
Abstract
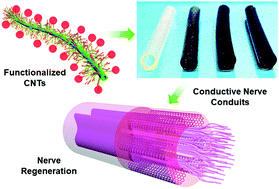
More than a million people are suffering from spinal cord injury (SCI) worldwide. However, currently there are no therapies that could ameliorate the neurological impairments, and the long-term SCI survival rate is far from satisfactory. Electrical stimulation and electrically conductive conduits are emerging as promising strategies with positive results showing increased neurite and axon growth in vitro and in vivo. In this study, we functionalized carbon nanotubes (CNTs) with hydrophilic poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) chains and further introduced crosslinkablility with double bonds. The final carbon-nanotube-poly(ethylene glycol)-acrylate (CNTpega) material was embedded within oligo(poly(ethylene glycol) fumarate) (OPF) at varying concentrations to form conductive hydrogels with modulable conductivities. The morphological properties, mechanical strengths, conductivities, and CNT distributions within the hydrogels were characterized. In vitro neural cell adhesion and proliferation as well as neurite development after nerve growth factor (NGF) induction showed significant enhancement in the conductive hydrogels. Various types of nerve conduits were then successfully fabricated using an injection molding technique. With many desired properties, these conductive nerve conduits have promising potential for promoting axon guidance and enhancing nerve recovery in spinal cord injury patients.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...