A facile fluorescence assay for rapid and sensitive detection of uric acid based on carbon dots and MnO2 nanosheets†
Abstract
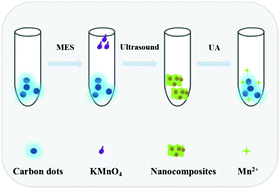
Uric acid (UA) is an important biological molecule in human pathology and is related to many critical diseases. Designing a simple and rapid method for sensitive UA determination is of great significance. Herein, we report a novel turn-on fluorescence assay for UA detection, based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between carbon dots (C-dots) and MnO2 nanosheets. MnO2 nanosheets can adsorb C-dots to form nanocomposites, where the fluorescence of C-dots is quenched via FRET. Fluorescence recovered when UA was introduced into the sensing system due to the decomposition of MnO2 nanosheets to Mn2+. Under optimized conditions, the fluorescence signal was linearly related to UA concentration in the range of 0.1–200 μM and the detection limit was as low as 45 nM. Moreover, this developed assay was successfully applied for human urine sample analysis, which indicated that this strategy could be an efficient tool for clinical disease diagnosis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...