Efficient removal of anti-inflammatory phenylbutazone from an aqueous solution employing a composite material based on poly(aniline-co-pyrrole)/multi-walled carbon nanotubes
Abstract
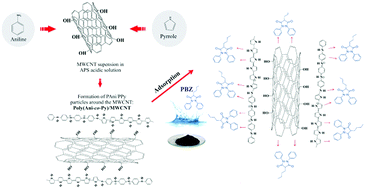
In this study, a composite based on poly(aniline-co-pyrrole)/multi-walled carbon nanotubes, named poly(Ani-co-Py)/MWCNT, was synthesized by chemical oxidation polymerization in a triple-phase interface system and evaluated as an adsorbent for the removal of phenylbutazone (PBZ) from an aqueous solution. To compare and understand the whole process, poly(Ani-co-Py)/MWCNT and pristine MWCNT were studied using adsorption and kinetic models. These materials were characterized by FTIR, TGA and SEM. Further studies involving adsorption on poly(Ani-co-Py)/MWCNT were conducted at pH 6 and on pristine MWCNT at pH 2. Under these conditions, the materials exhibited adsorption of PBZ above 90%. Kinetic studies showed that the adsorption mechanism for the PBZ reached equilibrium at about 60 min, characterizing a rapid absorption, which showed that PBZ had no resistance in transferring the aqueous phase to the material surface. The equilibrium adsorption data were best fitted with the dual-site Langmuir–Freundlich isotherm, with maximum adsorption capacities of 159.9 and 41.25 mg g−1, and constants related to the affinity for the drug of 0.099 and 0.178 L g−1, for poly(Ani-co-Py)/MWCNT and pristine MWCNT, respectively. Although the MWCNT has been reported in literature as an excellent adsorbent of various analytes, the poly(Ani-co-Py)/MWCNT presented a higher capacity for the removal of PBZ from an aqueous solution and a lower value related to its affinity for PBZ. This will possibly make it most suitable as an adsorbent in the sample preparation process using a suitable solvent for subsequent determination.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...