Synergism between luteolin and sulforaphane in anti-inflammation
Abstract
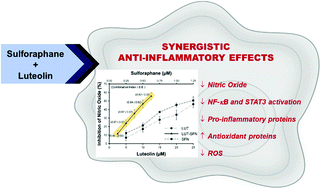
Luteolin and sulforaphane are well-known food bioactives with anti-inflammatory properties. Herein, we determined their combinational effects in inhibiting inflammation in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Both luteolin and sulforaphane showed dose-dependent inhibition on LPS-induced production of nitric oxide (NO) in the macrophages. The combined treatments led to a stronger inhibition on NO production compared to the singular treatments. Isobologram analysis confirmed that the combined treatments produced a synergy. Western blotting and ELISA showed that the combined treatment reduced the expression levels of pro-inflammatory proteins involving NF-κB pathway, and STAT3 activation, which regulated expression of other inflammatory proteins such as iNOS, COX-2, IL-6, and IL-1β. Moreover, the combination treatments reduced reactive oxygen species in cells and increased the expression of Nrf2 and HO-1, which are cellular antioxidant proteins. In conclusion, our findings support the notion that certain bioactive food components may act synergistically to produce enhanced health effects such as anti-inflammation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...