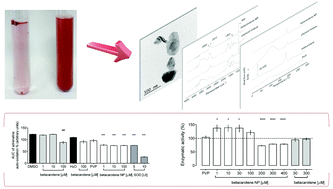
Beta-carotene is a carotenoid precursor of vitamin A, known for its biological activities. Due to its high hydrophobicity, nanonization processes, i.e. the transformation into nanoparticles, can improve its water affinity, and therefore the activity in aqueous systems. The objective of this study was to produce beta-carotene nanoparticles by the solid dispersion method and to evaluate their effects on the activity of glutathione-S-transferase and acetylcholinesterase enzymes using Drosophila melanogaster (DM) homogenate, the superoxide dismutase- and catalase-like activities under in vitro conditions, and their cytotoxic properties against tumor and non-tumor cells. The formed nanometric beta-carotene particles resulted in stable colloids, readily dispersed in water, able to modulate acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity, and presenting high potential to control the cholinergic system. Beta-carotene nanoparticles, at concentrations much lower than the pure pristine beta-carotene, presented in vitro mimetic activity to superoxide dismutase and altered glutathione-S-transferase activity in DM tissue. The content of hydrogen peroxide was neither affected by the nanoparticles (in aqueous solution) nor by pristine beta-carotene (in DMSO). In the cytotoxic assays, beta-carotene nanoparticles dispersed in water showed activity against four different tumor cell lines. Overall, beta-carotene nanoparticles presented significant bioactivity in aqueous medium surpassing their high hydrophobicity constraint.