Electric field mediated separation of water–ethanol mixtures in carbon-nanotubes integrated in nanoporous graphene membranes
Abstract
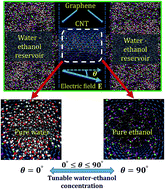
We investigate the influence of an applied electric field on the separation of a water–ethanol solution inside a carbon nanotube (CNT) using a series of molecular dynamics simulations. The electric field is applied at an angle θ with respect to the axis of the CNT. The study uncovers that with the application of a ‘small-angle’ electric field (e.g. smaller θ), the water molecules exhibit preferential occupancy inside the CNT, whereas the application of the same electric field at a ‘wide-angle’ mode (e.g. higher θ) fills the CNT with ethanol molecules in place of water. Remarkably, the direction of the electric field plays a pivotal role because the field exerts a contrasting influence on the behaviours of the water and ethanol molecules. The water dipoles are favourably aligned at small values of θ creating an ordered water structure inside the CNT. Increasing θ disrupts the water dipole orientation and leads to the preferential occupancy of the CNT by ethanol molecules. An in-depth analysis on the simulated systems unveil that, at lower values of θ, multiple layers of water molecules are physically adsorbed near the CNT walls, which is found to diminish as θ is increased. In comparison, at higher magnitudes of θ, the ethanol molecules are preferentially adsorbed inside the CNT. The average interaction energy per ethanol (water) molecule is found to increase (reduce) when θ is monotonically increased, which can be ascribed to the increase (decrease) in the intermolecular hydrogen bonding capacity of the ethanol (water) molecules at larger values of θ. Consequently, inside the CNT, the average occupancy of water molecules decreases and ethanol molecules increases, as θ is monotonically increased, leading to the separation of the ethanol–water mixture. The proposed methodology can convert an equimolar mixture (1 : 1) of ethanol–water into a concentrated one (14 : 1) when the electric field is applied orthogonal to the axis of the CNT. The separation efficiency is found to improve with an increase in the intensity of the externally applied electric field.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Artificial Water Channels


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...