Surface adsorption of Nordic aquatic fulvic acid on amine-functionalized and non-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles†
Abstract
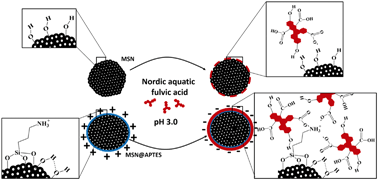
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) have the potential to be released into the environment and to then adsorb natural organic matter. Understanding the molecular–surface interactions that drive the kinetics and thermodynamics of the adsorption process is an important goal in developing models that accurately predict the fate and transport of these porous nanomaterials. Motivated by this goal, the adsorption of Nordic aquatic fulvic acid on amine functionalized and non-functionalized MSNs as a function of pH (3, 6 and 8) was studied using attenuated total reflectance Fourier transformation infrared spectroscopy. According to these results, carboxylic acid functional groups of Nordic aquatic fulvic acid and the amine functional groups on the functionalized MSNs play key roles in the adsorption process. Quantitative measurements were conducted using thermogravimetric analysis to determine the surface coverage of fulvic acid on the MSNs. The fulvic acid adsorption was pH dependent and decreased with increasing pH. Amine-functionalized MSNs exhibited a higher adsorption capacity of fulvic acid compared to the non-functionalized nanoparticles under all conditions. Furthermore, zeta potential measurements showed the impact of fulvic acid adsorption on the surface charge for these MSNs. Strikingly, the surface charge changed upon fulvic acid adsorption for amine-functionalized MSNs but remained constant for the unfunctionalized MSNs. Reasons for these differences and the overall environmental implications of this study are discussed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
