Copper(i) complexes with phosphine derived from sparfloxacin. Part III: multifaceted cell death and preliminary study of liposomal formulation of selected copper(i) complexes†
Abstract
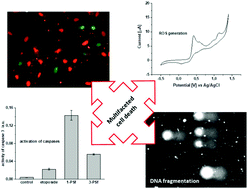
The cytotoxic effect of iodide or thiocyanate copper(I) complexes (1-PSf, 2-PSf, 3-PSf, 4-PSf) with phosphine derived from sparfloxacin (HSf) and 2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline (dmp) or 2,2′-biquinoline (bq) as diimine auxiliary ligands was proved in vitro on somatic (MRC-5) and neoplastic (MCF7) human cell lines. Differences in mode of action were investigated in-depth for the selected dmp and bq complexes (1-PSf, 3-PSf, respectively) by elucidation of the following: (i) the efficiency to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) in biological systems (cyclic voltammetry); (ii) their impact on mitochondrial membrane potential; (iii) potency for the activation of caspases 3 and 9; (iv) influence on the degree of DNA degradation (comet assay). It was concluded that the apoptosis of cancer cells is directly connected to the caspase-dependent mitochondrial pathway and supported by ROS production along with irreversible DNA fragmentation. Finally, it was demonstrated that the selected copper(I) complex encapsulated inside liposomes (1-PSf-L) exhibited enhanced accumulation inside cancer cells. This resulted in its higher cytotoxicity against cancer cells with therapeutic index of ca. 60. Increased selective accumulation in active neoplasm with simultaneous enhanced bioavailability and reduced systemic toxicity of liposomal formulation of copper(I) complexes can result in the development of new copper-based therapeutics and their successful implementation in anticancer chemotherapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...