Hydrogenation of CO2 into hydrocarbons: enhanced catalytic activity over Fe-based Fischer–Tropsch catalysts†
Abstract
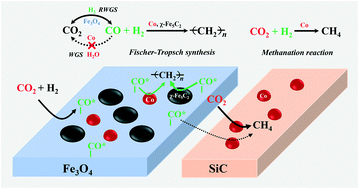
CO2-FTS is one of the most practical routes for converting CO2 into valuable chemicals and fuels to reduce CO2 emissions. However, efficient conversion remains a challenge because of its chemically inert property. Previously, we have reported a remarkably enhanced CO2 conversion efficiency by driving the RWGS reaction via the removal of large amounts of formed water in the reaction system. In this study, we propose to effectively enhance the CO2 conversion by promoting the conversion of the CO intermediate in the FTS stage. For this purpose, a K or/and Co (Ru) component is introduced onto the precipitated Fe catalysts. Results show that the addition of K obviously increases the CO2 conversion due to the promoted formation of iron carbide sites as the active FTS reaction phase. Moreover, the selectivity to C2+ hydrocarbons, especially lower olefins, can be substantially enhanced owing to the electron donation from K to Fe which promotes chain growth and suppresses the direct hydrogenation of Fe-(CH2)n intermediates. The addition of Co (Ru) that has no WGS activity could further remarkably enhance the CO2 conversion for Co (Ru) only promotes the FTS reaction rate of the CO intermediate without catalyzing the conversion of CO into CO2. Furthermore, the effects of the intimacy between Co and Fe sites from the nanoscale to the meter scale have also been investigated. The results display that the intimate contact between Fe and Co sites favors a higher selectivity to C2+ hydrocarbons, which is ascribed to the easy spillover of the CO intermediate from Fe3O4 to Co sites and thereby yielding a higher CO concentration over Co sites. In contrast, the increase in the distance between Fe and Co sites leads to a remarkably higher selectivity to CH4, which could be because the direct methanation of CO2 is enhanced and the chain growth possibility of the FTS reaction is reduced due to the lower CO concentration over Co sites.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...