Chemicals from lignin: an interplay of lignocellulose fractionation, depolymerisation, and upgrading†
Abstract
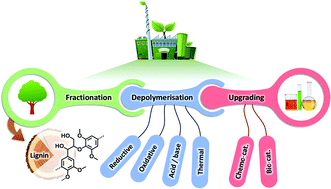
In pursuit of more sustainable and competitive biorefineries, the effective valorisation of lignin is key. An alluring opportunity is the exploitation of lignin as a resource for chemicals. Three technological biorefinery aspects will determine the realisation of a successful lignin-to-chemicals valorisation chain, namely (i) lignocellulose fractionation, (ii) lignin depolymerisation, and (iii) upgrading towards targeted chemicals. This review provides a summary and perspective of the extensive research that has been devoted to each of these three interconnected biorefinery aspects, ranging from industrially well-established techniques to the latest cutting edge innovations. To navigate the reader through the overwhelming collection of literature on each topic, distinct strategies/topics were delineated and summarised in comprehensive overview figures. Upon closer inspection, conceptual principles arise that rationalise the success of certain methodologies, and more importantly, can guide future research to further expand the portfolio of promising technologies. When targeting chemicals, a key objective during the fractionation and depolymerisation stage is to minimise lignin condensation (i.e. formation of resistive carbon–carbon linkages). During fractionation, this can be achieved by either (i) preserving the (native) lignin structure or (ii) by tolerating depolymerisation of the lignin polymer but preventing condensation through chemical quenching or physical removal of reactive intermediates. The latter strategy is also commonly applied in the lignin depolymerisation stage, while an alternative approach is to augment the relative rate of depolymerisation vs. condensation by enhancing the reactivity of the lignin structure towards depolymerisation. Finally, because depolymerised lignins often consist of a complex mixture of various compounds, upgrading of the raw product mixture through convergent transformations embodies a promising approach to decrease the complexity. This particular upgrading approach is termed funneling, and includes both chemocatalytic and biological strategies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...