The role of nitric acid in atmospheric new particle formation†
Abstract
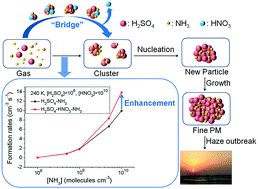
Nitric acid, an air pollutant with strong acidity and oxidizability, can be found in considerable quantities in the gas and aerosol phase. Understanding the role of nitric acid in atmospheric new particle formation is essential to study the complicated nucleation mechanism. Using density functional theory combined with the Atmospheric Clusters Dynamic Code (ACDC), the role of nitric acid in the formation of new particles has been investigated under different atmospheric conditions (different precursor concentrations and temperatures). The results show that nitric acid can form clusters with sulfuric acid and ammonia by hydrogen bond or even proton-transfer interactions. The concentrations of clusters involving nitric acid can be comparable with those of sulfuric acid–ammonia-based clusters, considering the thermodynamic stability combined with the realistic atmospheric concentrations of precursors. Within the atmospheric concentration range, nitric acid can enhance the formation rates of sulfuric acid–ammonia clusters, especially at low temperature, low sulfuric acid concentration and high ammonia concentration. In addition, the new particle formation mechanism indicates that nitric acid can contribute to the cluster formation and the role of nitric acid in the cluster formation pathway is as a “bridge” connecting the smaller and larger clusters.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...