CsPbBr3 and CH3NH3PbBr3 promote visible-light photo-reactivity†
Abstract
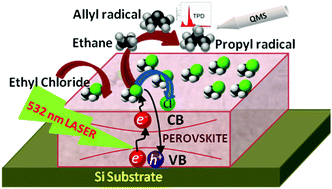
Inorganic and organic lead halide perovskite materials attract great interest in the scientific community because of their potential for low-cost, high efficiency solar cells. In this report we add a new property of these materials, namely their photochemical activity in the visible light range. Both inorganic (CsPbBr3) and organic (CH3NH3PbBr3-MAPbBr3) perovskite thin films were demonstrated to promote photo-dissociation of adsorbed ethyl chloride (EC), employing 532 nm pulsed laser irradiation under ultra-high vacuum (UHV) conditions. From the post-irradiation temperature programmed desorption (TPD) analysis, the yield of photoproduct formation was found to be up to two orders of magnitude higher than for UV light-excited EC molecules on metallic and oxide surfaces. Photo-reactivity on top of the CsPbBr3 surface is almost an order of magnitude more efficient than on the CH3NH3PbBr3 surface, apparently due to the lower density of defect and surface states. A direct correlation was found between electron-induced luminescence and photoluminescence intensities and the photoreactivity cross-sections. We conclude that both the intense luminescence and the well-known photovoltaic properties associated with these halide perovskite materials are consistent with the efficiency of photo-reactivity in the visible range, reported here for the first time.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...