Unique orientations and rotational dynamics of a 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium hexafluorophosphate ionic liquid at the gas–liquid interface: the effects of the hydrogen bond and hydrophobic interactions†
Abstract
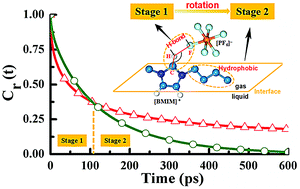
Here we report a series of molecular dynamics simulations for the orientations and rotational dynamics of the 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazoliumhexafluorophosphate ([BMIM][PF6]) ionic liquid (IL) at the gas–liquid interface. Compared to the bulk phase, the [BMIM]+ cations at the interface prefer to orientate themselves with their imidazolium rings perpendicular to the gas–IL interface plane and their butyl chains pointing toward the vacuum phase. Such a preferential orientation can be attributed to the combined effect of the hydrophobic interactions and the optimum loss of hydrogen bonds (HBs). More interestingly, our simulation results demonstrate that the butyl chains of cations exhibit a two-stage rotational behavior at the interface, where the butyl chains are always in the vacuum phase at the first stage and the second stage corresponds to the butyl chains migrating from the vacuum phase into the liquid phase. A further detailed analysis reveals that their rotational motions at the first stage are mainly determined by the weakened HB strength at the interface while those at the second stage are dominated by their hydrophobic interactions. Such a unique rotational behavior of the butyl chains is significantly different from those of the anions and the imidazolium rings of cations at the interface due to the lack of existence of hydrophobic interaction in the cases of the latter two. In addition, a new and simple time correlation function (TCF) was constructed here for the first time to quantitatively identify the relevant hydrophobic interaction of alkyl chains. Therefore, our simulation results provide a molecular-level understanding of the effects of HB and hydrophobic interactions on the unique properties of imidazolium-based ILs at the gas–liquid interface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...