Atomic charges for conformationally rich molecules obtained through a modified principal component regression†
Abstract
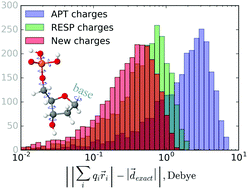
A modification of the principal component regression model is proposed for obtaining a fixed set of atomic charges (referred to as dipole-derived charges) optimized for reproducing the dipole moment of a conformationally rich molecule, i.e., a molecule with multiple local minima on the potential energy surface. The method does not require any adjustable parameters and requires the geometries of conformers, their dipole moments and atomic polar tensor (APT) charges as the only input data. The fixed atomic charges generated by the method not only reproduce the molecular dipole moment in all the conformers accurately, but are also numerically close to the APT charges, thereby ensuring accurate reproduction of the dipole moment variations caused by small geometrical distortions (e.g., by vibrations) of the conformers. The proposed method has been applied to canonical 2′-deoxyribonucleotides, the model DNA monomers, and the dipole-derived charges have been shown to outperform both the averaged APT and RESP charges in reproducing the dipole moments of large sets of conformers, thus demonstrating a potential usefulness of the dipole-derived charges as a ‘reference point’ for modeling polarization effects in conformationally rich molecules.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...