Recent progress in the self-assembly of block copolymers confined in emulsion droplets
Abstract
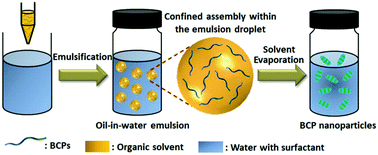
When the self-assembly of block copolymers (BCPs) occurs within a deformable emulsion droplet, BCPs can aggregate into a variety of nanoscaled particles with unique nanostructures and properties since the confinement effect can effectively break the symmetry of a structure. On the other hand, the self-assembled BCP particles can serve as the scaffolds to further direct the spatial arrangement of functional inorganic nanoparticles (NPs) via co-assembly or in situ deposition, thus generating diverse hybrid functional BCP/NP composites with enhanced properties. Here, we summarize the recent progress in the confined self-assembly of BCPs within the emulsion droplet and spatial arrangement of NPs on the resulting BCP scaffolds. This feature article focuses on the influence of multiple factors, including the oil/water interfacial properties, confinement degree, intrinsic properties of BCPs, additives, pH value, and temperature, on the nanostructures of the self-assembled BCP particles as well as the spatial arrangement of NPs on the BCP scaffolds from both experiment and simulation studies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...