Ruthenium-catalyzed selective α-deuteration of aliphatic nitriles using D2O†
Abstract
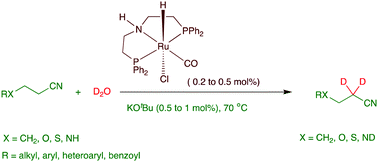
Selective catalytic α-deuteration of aliphatic nitriles using deuterium oxide as a deuterium source is reported. A PNP–ruthenium pincer complex catalyzed the α-deuteration of aliphatic nitriles including acetonitrile. Efficient deuteration occurred with a low catalyst load (0.2 to 0.5 mol%) and under mild conditions. A [2+2] cycloadduct formation from nitrile functionality and a deprotonated catalytic intermediate, followed by an imine–enamine tautomerization and a H/D exchange between the enamine intermediate and deuterium oxide leading to the selective deuteration at the α-position of the nitrile, is proposed as a plausible reaction mechanism.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...