Magnetic covalent organic framework material: synthesis and application as a sorbent for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons†
Abstract
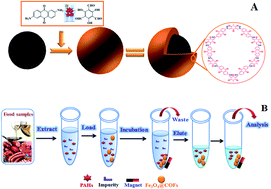
A novel magnetic covalent organic framework (Fe3O4@COF(TpDA)) material possessing a large surface area and high and regular porosity was constructed via a facile strategy and applied as a magnetic solid phase extraction sorbent for the determination of trace polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in edible oil and grilled meats prior to high performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection. The obtained materials were characterized by transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms and vibrating sample magnetometry. The prepared Fe3O4@COF(TpDA) materials showed some attractive features including a large surface area (180.20 m2 g−1) and high saturation magnetization (62.28 emu g−1). The experimental parameters affecting the extraction performance including the type of eluent, amount of sorbent, and adsorption and desorption times were optimized. Under the optimized conditions, the adsorption equilibrium for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons could be achieved in only 10 min. The proposed method achieved low limits of detection (0.03–0.73 μg L−1 for LODs and 0.10–2.43 μg L−1 for LOQs) and good linearity (R ≥ 0.9937). The obtained materials were successfully applied to enrich polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in edible oil and grilled meats and showed good accuracy with recoveries in the range of 85.5–104.2%. Furthermore, the proposed method was also evaluated by different adsorption kinetic theories, and the pseudo-second-order model can explain the adsorption kinetics. The proposed method is facile, rapid, effective and selective for determination of PAHs in food samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...