Ion mobility mass spectrometry workflows for characterizing bioactive isomer conformation, isomerization and drug–protein–liposome interaction†
Abstract
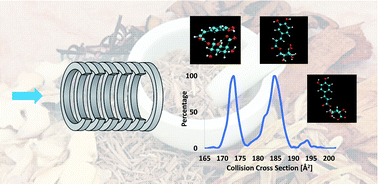
In drug discovery, understanding the drug structure is essential because it is closely associated with the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion properties of the drug. As a complex drug system, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has been effective in the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases in a synergic manner with milder healing effects and lower side effects compared to western medicines. The active components from TCM exhibit high structural diversity, while involving multiple isomers with the same molecular weights but different biological activities. In practice, these active compounds also undergo conformational changes and transformations. Thus it is important to estimate these structural changes and the related changes in biological interactions. In this study, we developed a novel strategy using ion mobility mass spectrometry (IM-MS) and molecular modeling for accurate characterization of conformational changes of TCM active isomers, their isomerization in degradation and the isomer–protein interactions. The relationship between the anti-inflammatory bioactivity and binding affinity to protein has been studied. Our work showed that IM-MS and molecular modeling can effectively differentiate structural isomers, associated conformation variants and their biological interactions with proteins and lipids. These workflows are essential for deeper pharmacological and toxicological understanding.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Analytical Methods Recent HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...