Preparation of an anti-formoterol monoclonal antibody for indirect competitive ELISA detection of formoterol in urine and pork samples
Abstract
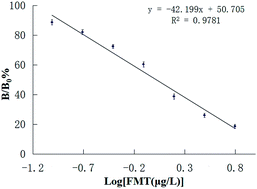
In this study, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was established to detect formoterol (FMT) residue in pork and urine samples. A monoclonal antibody (mAb) against FMT was prepared using hybridoma technology. The developed ELISA method had a standard curve ranging from 0.098 to 6.25 μg L−1. The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) value and the limit of detection (LOD) were 1.04 μg L−1 and 0.15 μg L−1, respectively. The cross-reactivity (CR) values of 7 compounds were less than 0.01%, but the CR value of clenbuterol was not (CR < 0.62%). Urine and pork samples supplemented with different concentrations of FMT were analysed using ELISA. The intra-assay recovery rates and coefficients of variation were in the range of 91.5–118% (n = 5) and 7.9–14.7% (n = 5), respectively. In contrast, the inter-assay recovery rate ranged from 87% to 124% (n = 5), and the coefficients of variation were within 6.3–18.6% (n = 5), indicating that the assay had high accuracy and precision. Correlation values for urine and pork were higher (R2 = 0.99 and 0.98, respectively) for the optimized ELISA than for standard LC-MS/MS analysis in a variety of samples. This optimized mAb-based ELISA provides a rapid method for detecting FMT residue in urine and pork samples with high specificity and sensitivity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...