In vitro antibacterial activity of oxide and non-oxide bioceramics for arthroplastic devices: II. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
Abstract
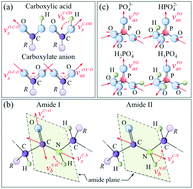
The metabolic response of Gram-positive Staphylococcus epidermidis (S. epidermidis) bacteria to bioceramic substrates was probed by means of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Oxide zirconia-toughened alumina (ZTA) and non-oxide silicon nitride (Si3N4) substrates were tested. Bacteria exposed to silica glass substrates were used as a control. S. epidermidis, a major cause of periprosthetic infections, was screened to obtain a precise time-lapse knowledge of its molecular composition and to mechanistically understand its interaction with different substrates. At the molecular level, the structure of proteins, lipids, nucleic acid, and aromatic amino acids evolved with time in response to different substrates. In combination with statistical validation and local pH measurements, a chemical lysis mechanism was spectroscopically observed in situ on the Si3N4 substrates. Utilization of FTIR in this study avoided fluorescence noise which occurred while probing the ZTA samples with Raman spectroscopy in a companion paper. The substrate-driven dynamics of polysaccharide and peptide variations in the bacterial cell wall, peculiar to Si3N4 bioceramics, are elucidated.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...