High dielectric constant and low dielectric loss poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanocomposites via a small loading of two-dimensional Bi2Te3@Al2O3 hexagonal nanoplates
Abstract
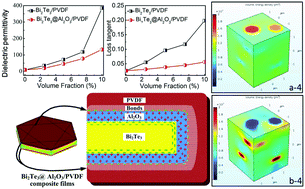
Two-dimensional (2D) core–shell structure Bi2Te3@Al2O3 nanoplates were synthesized from 2D Bi2Te3 nanoplates via a sol–gel method, where the 2D Bi2Te3 nanoplates were prepared via a microwave-assisted method. Homogeneous nanocomposite films, with poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) as the polymeric matrix and Bi2Te3 nanoplates or core–shell structured Bi2Te3@Al2O3 nanoplates as the fillers, have been prepared. The dielectric behavior of the Bi2Te3/PVDF and Bi2Te3@Al2O3/PVDF nanocomposites has been investigated. Compared with the Bi2Te3/PVDF nanocomposite, the Bi2Te3@Al2O3/PVDF composite film exhibits larger breakdown strength and lower dielectric loss, due to the highly insulating Al2O3 shell layer, as well as the Al2O3 dielectric constant being incorporated into the Bi2Te3 nanoplate surface. As a result, the composite film loaded with 10 vol% 2D Bi2Te3@Al2O3 nanoplates exhibits a high dielectric constant of 140 and a relatively low dielectric loss of 0.05 at 1 kHz. Furthermore, finite element simulations were carried out to understand the dielectric mechanism of Al2O3 shell layer effects on the dielectric performances of the nanocomposite films. This study provides a solution for obtaining high-k dielectric composites with low dielectric loss, which is highly desired for power systems and advanced electronics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...