Unlocking the structure of mixed amorphous-crystalline ceramic oxide films synthesized under low temperature electromagnetic excitation†
Abstract
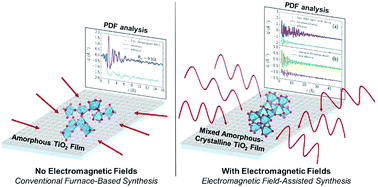
The promise of using electromagnetic (EM) fields for low temperature materials synthesis is limited by our ability to structurally characterize these materials, which are often nanocrystalline or amorphous. Here we demonstrate that synchrotron X-ray radiation coupled with the recently developed thin film pair distribution function (tfPDF) analysis yields quantitative information about mixtures of crystalline and non-crystalline materials synthesized under EM excitation, which represents a new direction to study the chemical reactions and lattice ordering induced by EM fields. Our experiments demonstrate for the first time that ceramic oxide films of titanium dioxide (TiO2) grown under microwave radiation (MWR) exposure contain a different phase composition and increased crystallinity compared to TiO2 grown at similar temperatures without EM fields. Specifically, the field-assisted TiO2 is composed of a mixed-phase structure consisting of long-range anatase TiO2 phase with short-range amorphous components, while furnace-grown materials are amorphous with local ordering most resembling the brookite phase of TiO2. The disordered component of MWR-grown TiO2 results in a slightly narrower energy band gap relative to fully crystalline anatase, indicating enhanced light absorption in the visible spectrum. The impact of EM field-influenced atomic structure on resultant material properties creates the opportunity to utilize MWR-assisted synthesis as a novel method for rapid, single-step, low temperature synthesis of mixed ordered-disordered materials for potential use in photocatalysis, thermoelectrics, or lithium ion batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...