Modification of LSCM–GDC cathodes to enhance performance for high temperature CO2 electrolysis using solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOECs)†
Abstract
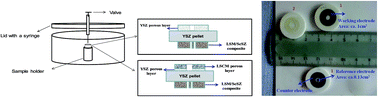
Extensive efforts have been made to find new fuel electrode materials for solid oxide cells with high activity and durability to provide more robust materials than state-of-the-art materials, Ni-cermets. In the present study, a Ni-free cathode with competitive performance and higher durability than a well performing Ni–YSZ cermet for CO2 electrolysis using SOECs is prepared. A (La, Sr)(Cr, Mn)O3/(Gd, Ce)O2 (LSCM/GDC) cathode fabricated by vacuum infiltration of GDC nitrate solutions into a LSCM/YSZ (8 mol% yttria stabilised zirconia) skeleton is reported. A porous YSZ layer introduced between the dense electrolyte and this cathode helps to maintain a good cathode/electrolyte interface, whilst the nano-structured GDC phase introduced on the surface of the LSCM/YSZ backbone is advantageous to boost the electrochemical and catalytic properties of the cathode towards CO2 reduction using SOECs. Vacuum impregnation therefore offers an effective means to modify the microstructure of the LSCM/GDC material used as a cathode for high temperature CO2 electrolysis. With the doping of a Pd co-catalyst after GDC impregnation, the cathodic activity of the GDC impregnated LSCM material is further enhanced for high temperature CO2 electrolysis, and the 0.5 wt% Pd and GDC co-impregnated LSCM cathode achieves an Rp value of 0.24 Ω cm2 at OCV at 900 °C in a CO2–CO 70–30 mixture, a comparable level to that of a high performance Ni–YSZ cathode operated under identical conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...