Design of yield-stress fluids: a rheology-to-structure inverse problem†
Abstract
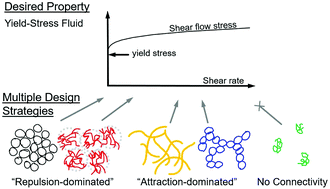
We present a paradigm for the design of yield-stress fluids, using six archetypal materials for demonstration. By applying concepts of engineering design, we outline a materials design paradigm that includes (i) morphological organization based on jammed versus networked microstructures, (ii) collected scaling laws for predictive design, (iii) low-dimensional descriptions of function-valued flow data, (iv) consideration of secondary properties including viscous behavior, and (v) a strategy for material concept synthesis based on the juxtaposition of microstructures. By explicitly specifying these design strategies, we seek to create an ontology and database for the engineering of yield-stress fluids. Our proposed design strategy increases the likelihood of finding an optimal material and prevents design fixation by considering multiple material classes to achieve a desired rheological performance. This flips the typical structure-to-rheology analysis to become the inverse: rheology-to-structure with multiple possible materials as solutions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...